Study on environmental risk factors and metabolomics by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry
Causal relationship when the tandem mass spectrometry meets environmental toxicology and metabolomics
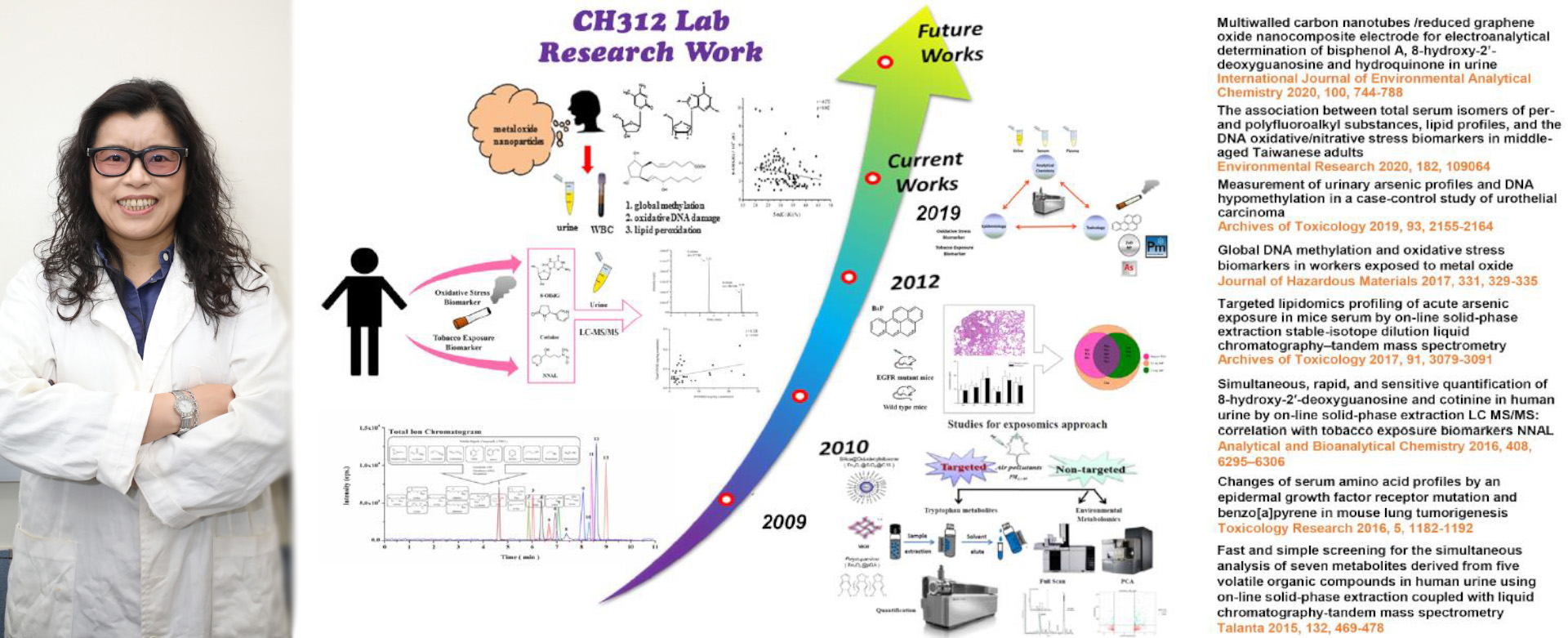
Many diseases are closely related to the environment, such as lung cancer, which is one of the top ten causes of death in Taiwan. Causes include heavy metals, nanoparticles, second-hand smoke, suspended particles, volatile organic compounds and other risk factors in the living environment. This research focuses on finding a suitable biomarker to assess these factors and their human physiological effects.
In order to understand the effects of environmental pollutants on the human body, with the help of liquid chromatography mass spectrometry platform technology, Professor Hui-Ling Lee explores the correlation between various types of metabolomics through the comprehensive metabolic profile analysis of the human body and animal exposure to environmental pollutants to find novel biomarkers such as amino acids, tryptophan metabolites, arachidonic acid metabolites and perfluorocarbon compounds, and is committed to developing a new target body metabolism metabolomics method and discussing the influence of environmental risk factors when the method is applied to different aspects of epidemiological models. When the particles enter the lungs through the respiratory system, the toxic chemicals adsorbed by the particles induce the production of reactive oxygen species and initiate a series of free radical reactions that damage a person's DNA and cell structure, leading to the generation of oxidative damage index 8-OHdG (8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine), 8-isoPGF2α (8-iso-prostaglandin F2α) and epigenetic methylated DNA.
In the field of analytical chemistry, the sample pretreatment is an important link. Whether the interference in the sample can be effectively eliminated in the complete analytical process takes 40-60% of the time of the whole process, thus affecting the qualitative and quantitative quality. Therefore, novel extraction methods are developed, such as the distributed solid-phase extraction, magnetic solid-phase extraction, and development of special materials such as a metal-organic framework (MOF), Fe3O4@PDA (Iron oxide coating polydopamine), Fe3O4@C18 and Fe3O4@APTES.
[Future Outlook]:
- Research of environmental toxicology and metabolomics
- Development of tandem mass spectrometry
- Development of sample pretreatment technology
- Practical application of analytical techniques