Featured Scientist

Tsai-Hua Kao, Ph.D.
Professor
Beer Brewing Byproducts, Not Only for Animal Feed -Health potential
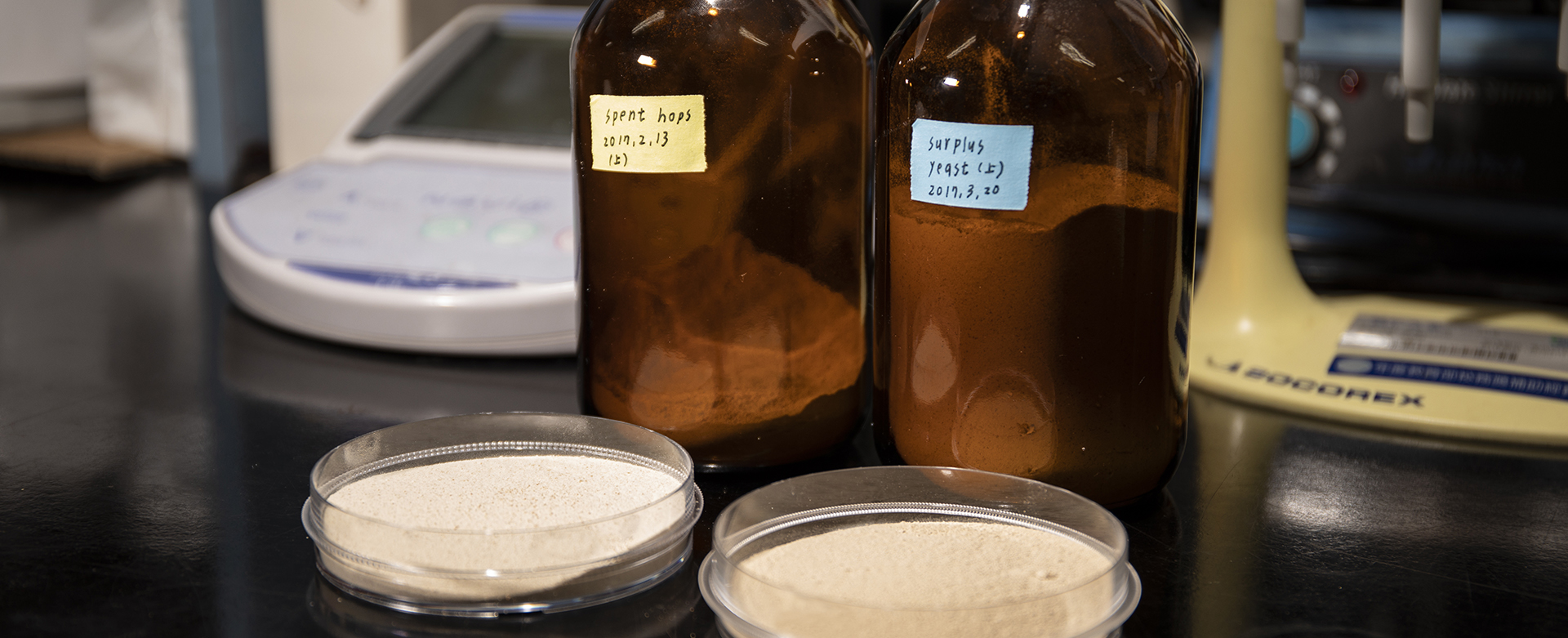
Beer brewing byproducts
The beer brewing process involves malting, milling, mashing, boiling, cooling, and fermentation. Approximately 20 kg of byproducts are produced for every 100 liters of beer brewed, of which brewer’s spent grains (SG), spent hops (SH), and surplus yeasts (SY). Most of these byproducts are used as animal feed and fertilizers since insufficient research has been devoted to the physiological activities for human.
Functional components in beer brewing byproducts
SG is rich in cellulose, protein, phenolics and mineral; SH is rich in fiber and protein; SY is rich in proteins and saccharides; where both SH and SY also are rich in prenylflavonoids and hop bitter acids.
To date, a total of 4 prenylflavonoids as well as 20 hop bitter acids and their derivatives could be found and analyzed within 30 minutes by employing our system, which possessed satisfactory resolution, accuracy, and precision.
Antiobesity effect of beer brewing byproducts
Animal models have proven that feeding extract from mixture of SH and SY could reduce the weight of fat around the kidneys and paraplegia, reduced triglyceride content in serum and the liver, and increased antioxidant capacity in the liver.
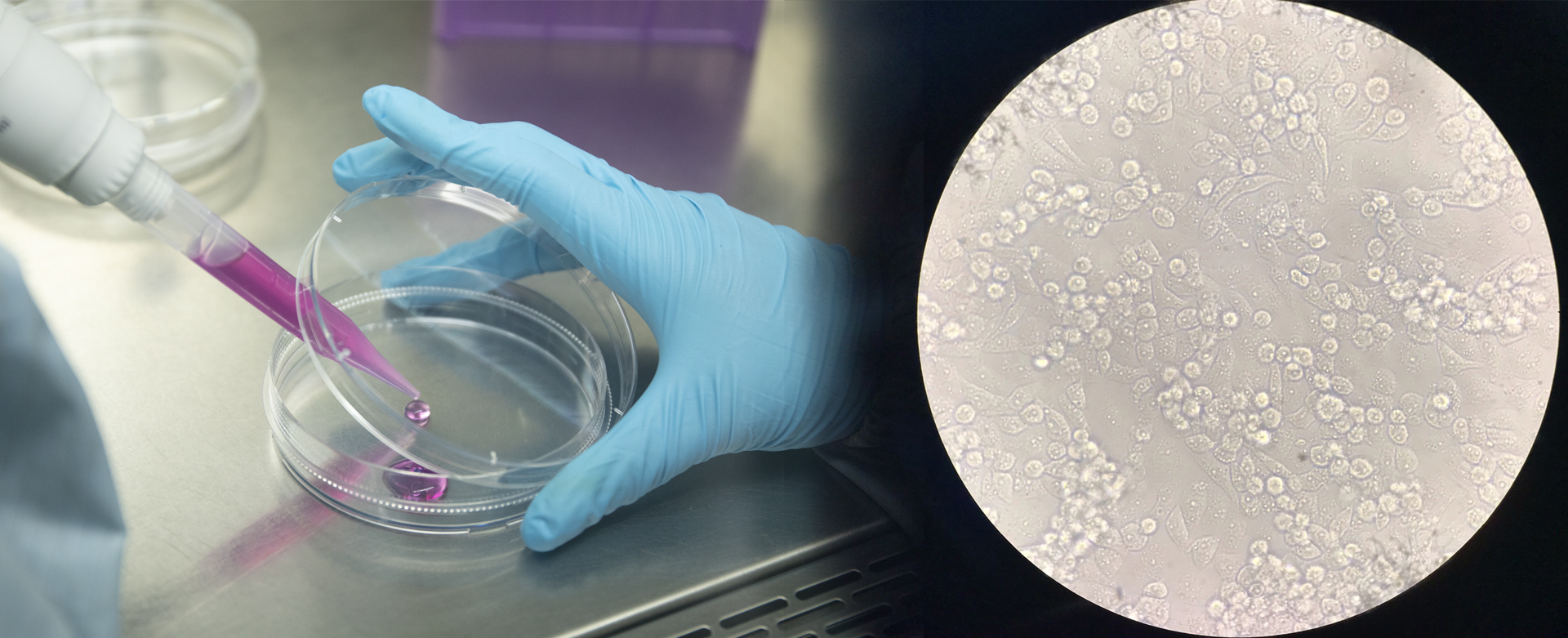
Antiproliferation of lung cancer cells by beer brewing byproducts
SY extract reducing the survival of both A549 and H460 lung cancer cells. The inhibition mechanism including by increased the expression of p-ERK1/2, p-JNK, and p-p38, suppressed the expression of cyclins and arrested the cell cycle for cancer cells. The main suppressants were xanthohumol and hop bitter acids
Publication
1. Kao, T. H.*, G. Y. Wu. 2013. Simultaneous determination of prenylflavonid and hop bitter acid in beer lee by HPLC-DAD-MS. Food Chem. 141:1218-1226. SCI.
2. Kao, T. H.* 2018. Health Potential of Byproducts from Beer Brewing. In: Current topics on superfoods. pp. 49-66. Ed. By N. Shiomi. IntechOpen. Londen.
95 views