Featured Scientist
Hui-Li Lin
Hui-Li Lin
Department of Clinical Psychology
Fu Jen Catholic University, New Taipei City, Taiwan
Social Interaction in Different Contexts of Screen-Media Activities: The Case of Chinese-Heritage Children and Caregivers in Taiwan
ABSTRACT
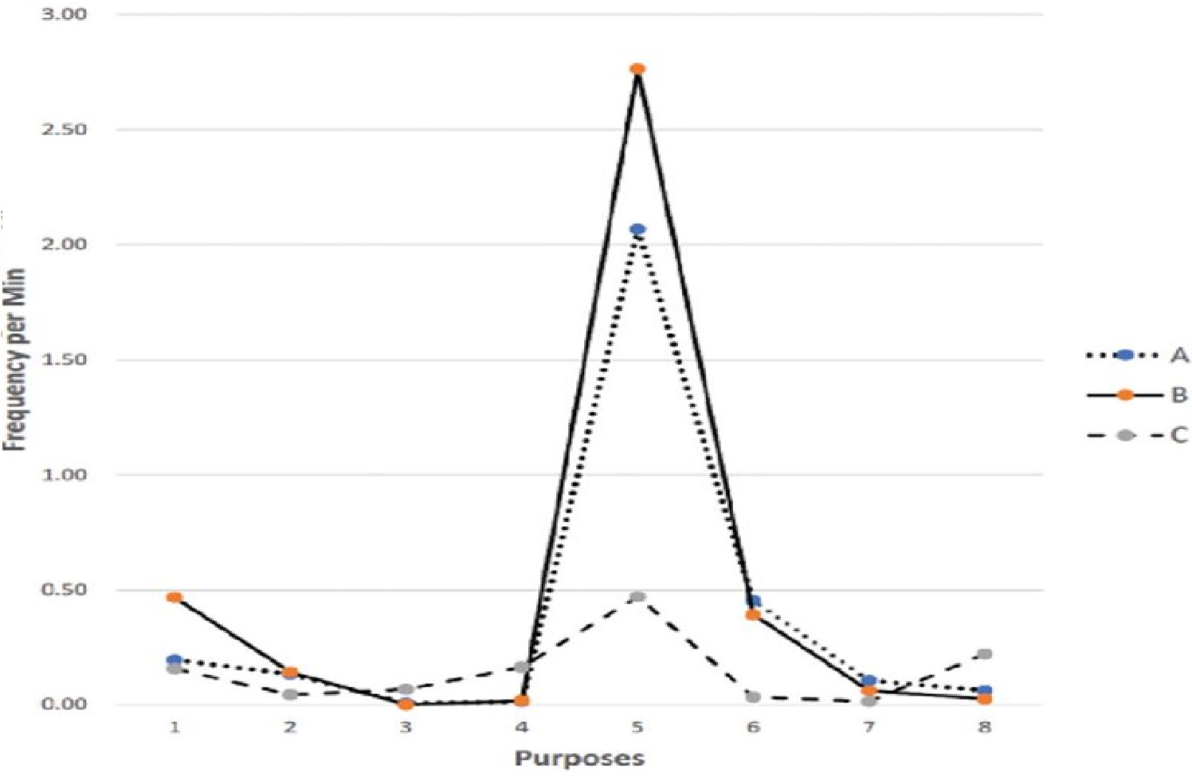
In many communities, children increasingly use digital devices for the purposes of playing and learning. The present study investigated Taiwanese preschool-aged children’s social interactions with caregivers during screen-media activities. Forty-five 3- to 6-year-olds and their caregivers played with a non-educational game app, an educational game app, or watched an educational video together. Child- and caregiver-initiated social behaviors were coded to examine (1) developmental changes in social interactivity initiated by children, (2) whether social interactivity varies depending on the activity context, and (3) the role caregivers play in maintaining social interactivity during these activities. The results showed that at preschool age, children still treated device use as a social activity, although the level of interaction has subsided since toddlerhood. Playing with an educational game was the context in which we observed higher interactivity, for which caregivers played a key role. These patterns are interpretated with a cultural lens, connecting to cultural practices unique to Chinese-heritage families.
IMPACT SUMMARY
Prior Statement of Knowledge: Toddlers in the U.S. initiated social interactions with an unfamiliar adult when playing with a non-educational game app. They did so to share success, request help, or invite the adult to participate in the gaming activity.
Novel Contributions: Preschool-aged children in Taipei, Taiwan initiated social interactions to share and request help with their caregiver, more frequently when playing an educational game app. Caregivers were actively engaged in supporting social interactivity, providing instruction and encouragement.
Practical Implications: Social interactivity during device use may decline as children age. However, caregivers can serve a key role in making screen-media activities a social context for children, thereby helping to turn screen time a context for social interaction.
Keywords:technology use, social behavior, caregiver-child interaction, preschool age, touch screen
4 views