Featured Scientist

Wei-Chi Ku, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
LC-MS/MS for Precision Medicine
With recent advances in instrument and analytical strategy, mass spectrometry (MS) has been an indispensable technology in clinical chemistry, ex. therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM), as well as biomedical research, such as quantitative proteomics. By applying state-of-art MS technologies, we explore several research topics as follows:
Precision medicine of renal cell carcinoma
In Taiwan, renal cell carcinoma (RCC) accounts for 1.26% of all cancer cases annually. Although surgery is considered as the best management for primary RCC, patients may develop recurrent and metastatic RCC (mRCC) in 2 to 5 years after nephrectomy. Patients with mRCC are resistant to conventional chemotherapy and radiotherapy. By using first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors and mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors, it makes possible for the treatment of mRCC.
For each patient with RCC, he or she may carry individualized signaling alteration, which can affect the therapeutic efficacy as well as prognostic results. The sequence of the most optimal therapies still remains highly challenging issue, especially on the quick development of drug resistance in mRCC patients. We take advantage of quantitative phosphoproteomics to construct Taiwan-localized and personalized RCC “phospho-barcode” database, and screen for novel drug targets for managing RCC.
Development and application of TDM methods
In the past decade, there is increased recognition that LC-MS based TDM is important in wide applications in clinical tests. By using selected reaction monitoring (SRM) approach, LC-MS provides highly sensitive and selective detection of drug targets in complex biological samples, such as blood and tissue.
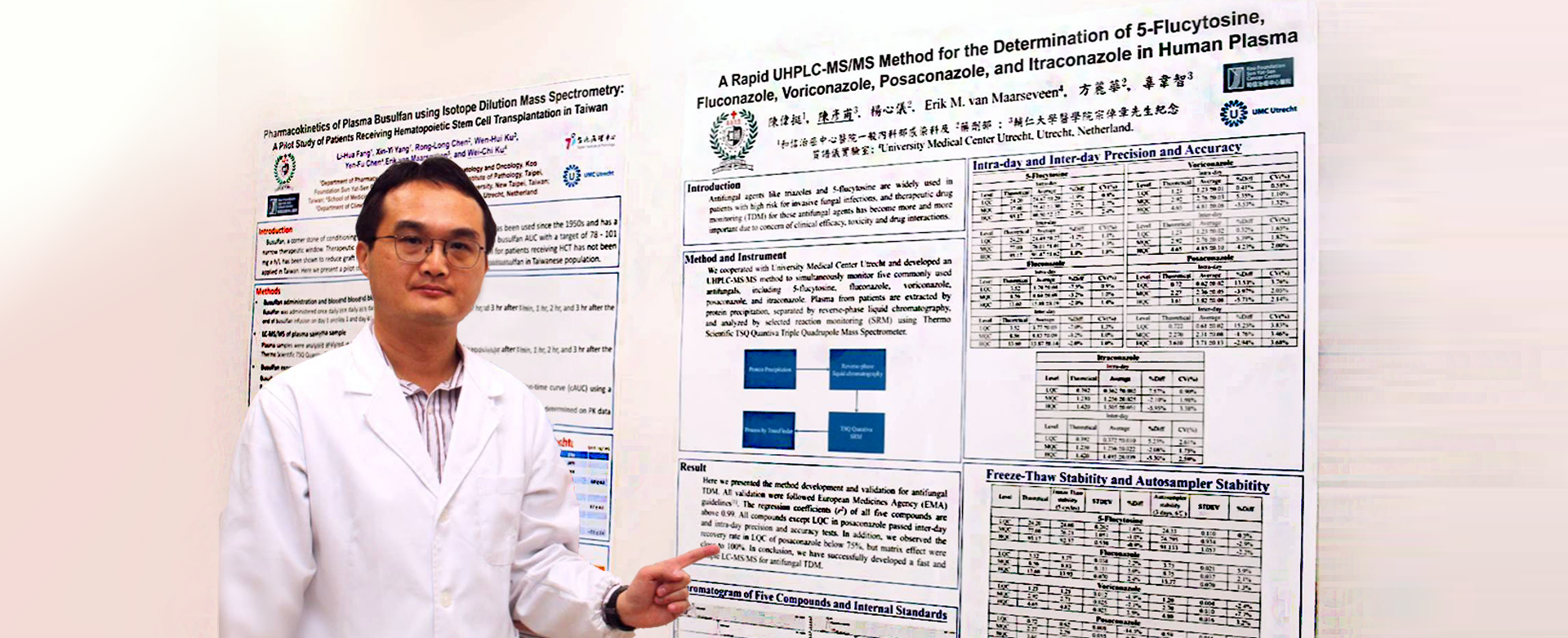
We have been cooperated with world-leading clinical chemistry laboratory and developed TDM method for simultaneous quantitation of five commonly-used anti-fungal agents, as well as temporal measurement of busulfan for conditioning of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
With the success of application in several TDM methods, we take a step forward to develop TDM methods for accurately quantitate active form of monoclonal antibody drug in patient blood samples. Currently, we focus on the drugs for treating rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowl disesases.
120 views