Featured Scientist

Author published in"International Journal of Hospitality Management"affiliate to
Chi-Mei Emily Wu
Department of Restaurant, Hotel and Institutional Management,
Fu Jen Catholic University, New Taipei City, Taiwan
Article published in
"International Journal of Hospitality Management" Volume 86, April 2020, Article number:102430
Why hotels give to charity: Interdependent giving motives
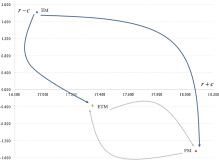
Previous studies assume that the motives behind corporate giving (CG) are independent, ignoring possible interactions and probably resulting in less accurate analyses. Therefore, this study uses analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and decision-making trial and evaluation laboratory (DEMATEL) techniques to evaluate the relative importance and the interdependence of the critical motives behind hotel giving in Taiwan. This study presents three findings: (1) giving motives are highly interdependent; (2) economic motive is a cause; philanthropic and ethical motives belong to effect group; and (3) the philanthropic motive (0.368) is the most important, followed by economic (0.340) and ethical (0.292) motives. In short, hotels have a higher propensity to moral values in CG but without losing sight of their financial performance. Moreover, the economic outcome of CG is the core motive. Not only does it directly influence CG; it also indirectly affects CG through the other two effect motives.[Full article]

Keywords : AHP and DEMATEL, Critical motives,Hotel giving, Interdependence, Relative importance
41 views