Featured Scientist

Author published in"Biochemical Pharmacology"affiliate to
Chia-Chia Chao
Department of Respiratory Therapy,
Fu-Jen Catholic University, New Taipei City, Taiwan
Article published in
"Biochemical Pharmacology" Volume 166, August 2019, Pages 23-32
Thrombospondin enhances RANKL-dependent osteoclastogenesis and facilitates lung cancer bone metastasis
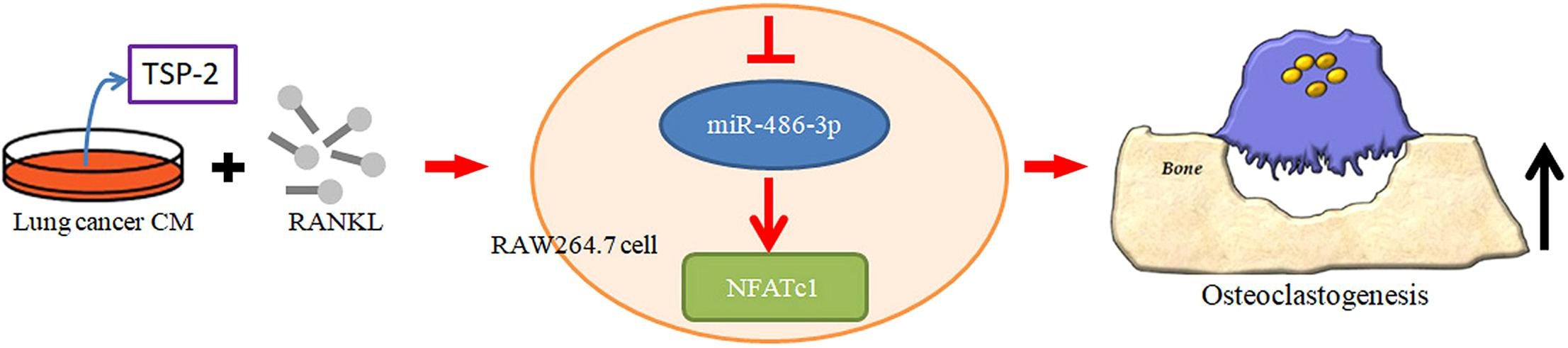
Lung cancers have a predilection for metastasizing to bone. The matricellular glycoprotein thrombospondin (TSP)-2 regulates multiple biological functions and has a critical role in tumor development and metastasis, although its effects are uncertain in lung cancer bone metastasis. This study demonstrates that TSP-2 expression is highly correlated with lung cancer tumor stage and that the TSP-2 neutralizing antibody reduces osteoclast formation in conditioned medium obtained from lung cancer cells. We also found that TSP-2 promotes osteoclastogenesis through the RANKL-dependent pathway and that TSP-2-mediated osteoclastogenesis involves the transactivation of nuclear factor of activated T-cells cytoplasmic 1 (NFATc1) via the inhibition of miR-486-3p expression. Osteoblasts played a critical role in osteoclast differentiation and incubation of osteoblasts with TSP-2 altered the RANKL:OPG ratio. Furthermore, TSP-2 knockdown inhibited lung cancer osteolytic metastasis in vivo. TSP-2 appears to be worth targeting for the prevention of bone metastasis in lung cancer.[ Full article]
keywords : Thrombospondin, Lung cancer, Osteoclasts, Bone metastasis, miR-486-3p
33 views