Featured Scientist

Chi-Shun Tu, Ph.D.
College of Science and Engineering
Distinguished Professor
Experiences
2012/02~2015/07 Dean of Research and Development, Fu-Jen Catholic University
2008/08~2012/01 Director of the Graduate Institute of Applied Science and Engineering, Fu-Jen Catholic University
2004/08~The Graduate Institute of Applied Science and Engineering
2000/08~ Professor, Department of Physics, Fu-Jen Catholic University
1995/08~2000/07 Associate Professor, Department of Physics, Fu-Jen Catholic University
Education & Academic Qualifications
1980/08~1985/06 Bachelor of Physics, National Taiwan Normal University, Taiwan.
1988/08~1990/06 Master of Physics, University of Oregon, USA.
1990/08~1994/12 PhD in Physics, Montana State University, USA.
Research Interests
Light scattering, Ferroelectric materials
研究方向與內容
1. ITO薄膜/BiFeO3陶瓷/Au薄膜之異質結構的光電能量轉換與機制理論
內容: Power conversion efficiency (PCE), External quantum efficiency (EQE)
Open-circuit voltage, Short-circuit current density, Domain structure, Raman spectroscopy, Photoluminescence, X-ray synchrotron absorption, Transmission electron microscopy.
2. Bioactive glass-ceramics
內容: CaO-SiO2-P2O5 (CSP) & CaO-MgO-SiO2 (CMS) bioactive glass-ceramics
重要學術/實務經驗及成果
1. 輔仁大學傑出研究獎 (107年)
2. 輔仁大學學術特聘教授 (107年8月1日起)
3. 科技部特殊優秀人才獎勵 (99109年)
近年研究主要突破是ITO薄膜/Nd-doped BiFeO3 (BNFO)陶瓷/Au薄膜之異質結構在紫藍光( = 405 nm)照射下,最大光電功率轉換效率(power conversion efficiency, PCE)及外部量子效率(external quantum efficiency, EQE)。這些光伏參數是目前多晶向(polycrystalline)鐵電材料中最大的光伏效應實驗值。依據光學穿透與光致發(photoluminescence)光譜,陶瓷的光學能隙(optical bandgap, Eg)。學理創新方面,我們發展p-n-junction model理論及polarization-induced Schottky-barrier 模型解釋電場極化增強光伏效應及能量轉換效率的物理機制。同時使用synchrotron soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy (新竹國家同步輻射中心BL20A1)、high-resolution TEM、micro-Raman spectroscopy等高解析分析實驗,探討極化電場對BNFO陶瓷晶粒內部microstructure、microdomains、orbital hybridizations及vibrational modes等微觀物理性質影響,提供多鐵性BiFeO3材料在光電能量轉換及光觸媒(photocatalyst)重要學術及應用參數,研究成果近期已發表於國際知名材料領域期刊Acta Materialia (Impact Factor=7.656; Journal Rank: 1/79)。
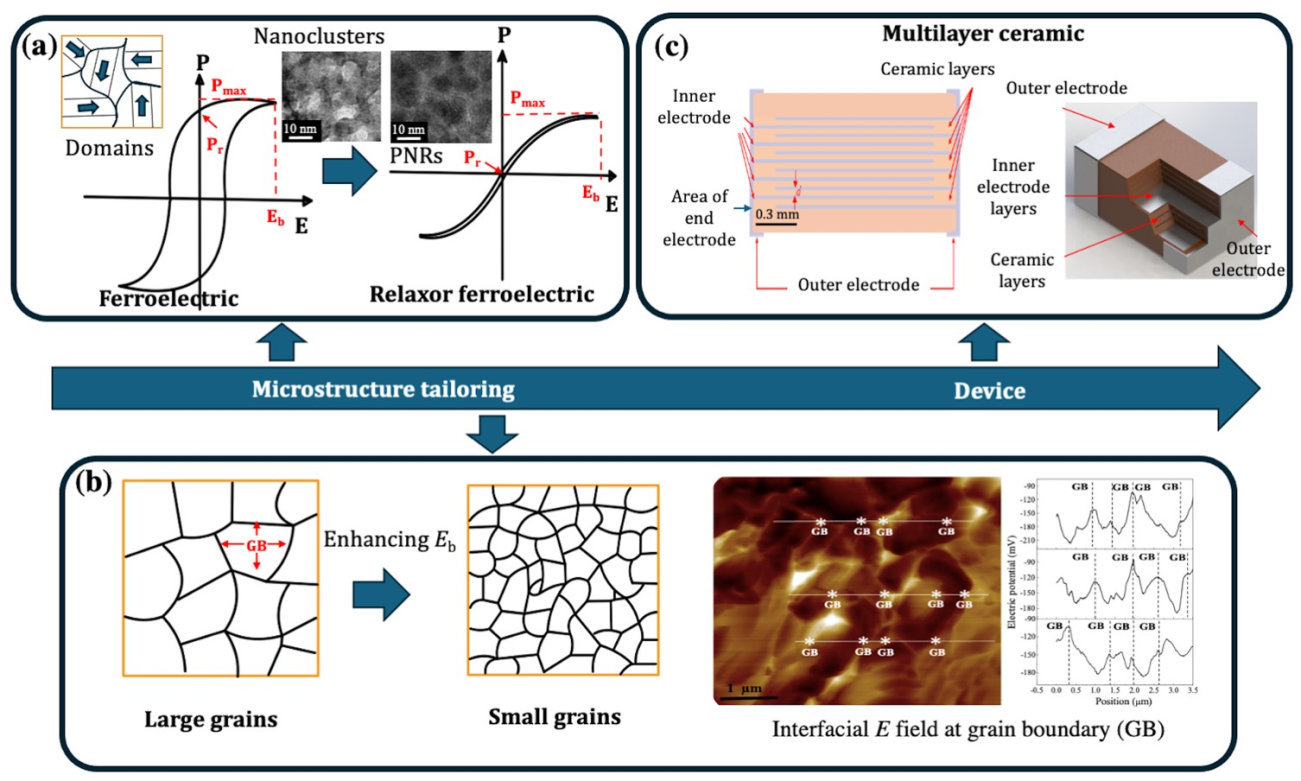
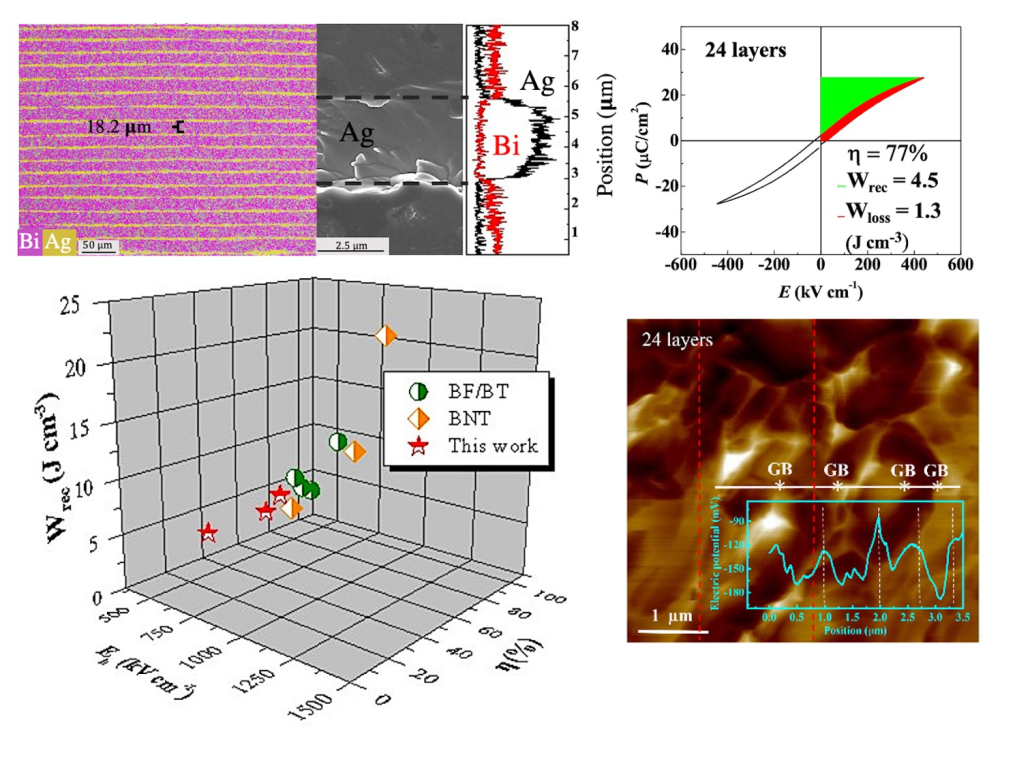
Ultrahigh energy storage in multilayer BiFeO3-BaTiO3-NaTaO3 relaxor ferroelectric ceramics
The rising challenge of high-density electric energy storage has accelerated the research of electric energy-storage capacitors due to their high-power density and voltage resistance, excellent temperature stability, and environmental friendliness. However, lead-free ferroelectric capacitors generally have a low discharge energy density. This study used the multilayer-ceramic-capacitor (MLCC) design with active ceramic layers of the relaxor ferroelectric NaTaO3-modified BiFeO3-BaTiO3 co-sintered with 90Ag/10Pd interlayer electrodes. Superb recoverable energy densities of Wrec ~ 2.8 J cm-3 with an energy efficiency of η ~ 73% at 400 kV cm-1 and Wrec ~ 4.5 J cm-3 with an energy efficiency of η ~ 77% at 450 kV cm-1 were attained respectively in the 9-active-ceramic-layer and 24-active-ceramic-layer MLCCs. Excellent thermal stability and fatigue resistance of energy storage capability were achieved up to 180 oC and exceeding 1×104 cycles. The ultrahigh energy-storage properties can be linked to the synergistic effects of multiple local lattice distortions, nanoscale structures, and interfacial E fields at grain boundaries. This report demonstrates an efficient scheme to utilize ternary BiFeO3-BaTiO3-based ceramics via the MLCC technology for ultrahigh-energy-density electrostatic energy storage.
Keywords:BiFeO3-BaTiO3-NaTaO3, Multilayer, Breakdown strength, Energy density, Efficiency
4 views