A rat model with total parenteral nutrition infusion
Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) is a vital feeding technique for individuals who cannot absorb sufficient nutrients from the gastrointestinal tract. TPN, a hypertonic solution administered via a central venous catheter, has been used in clinical medicine and specific indications for over two decades. However, the immunosuppressive effects of TPN and the prolonged administration of TPN solution increased risk of cholestasis, hepatic steatosis, and liver dysfunction have been draw a lot of attentions.
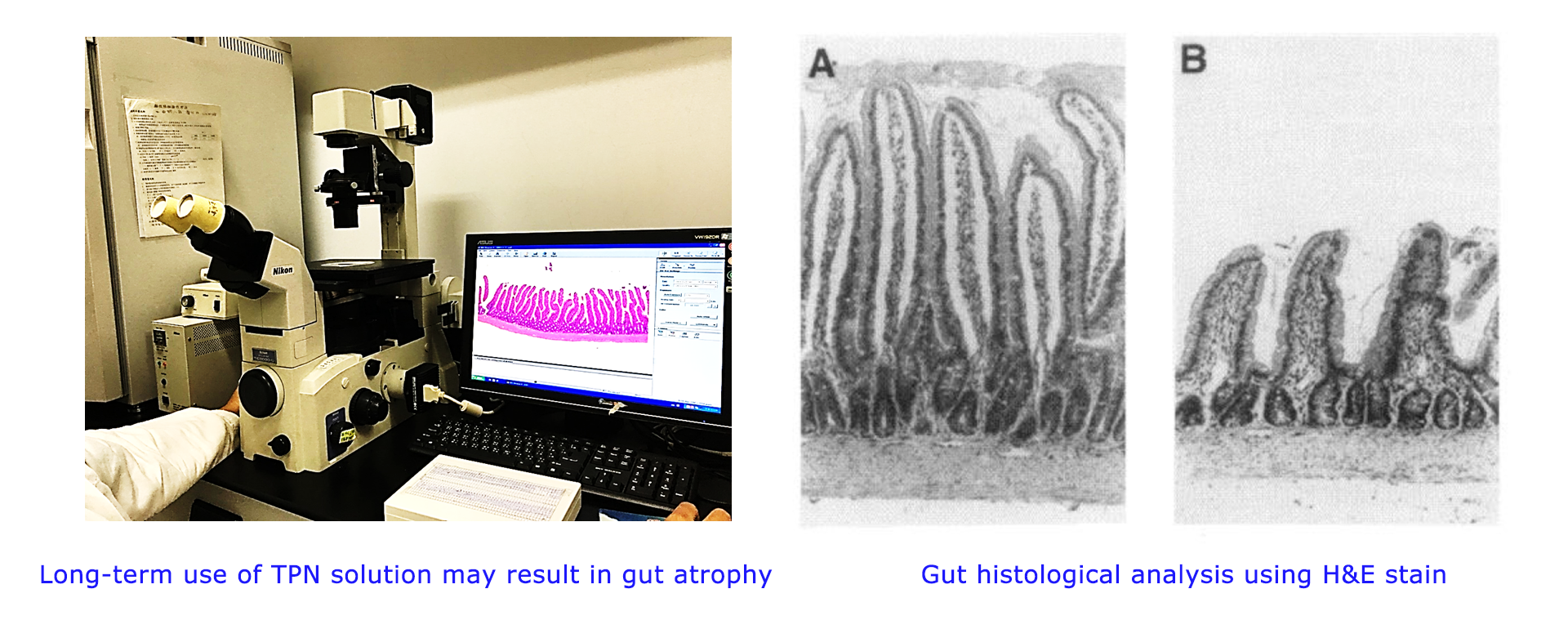
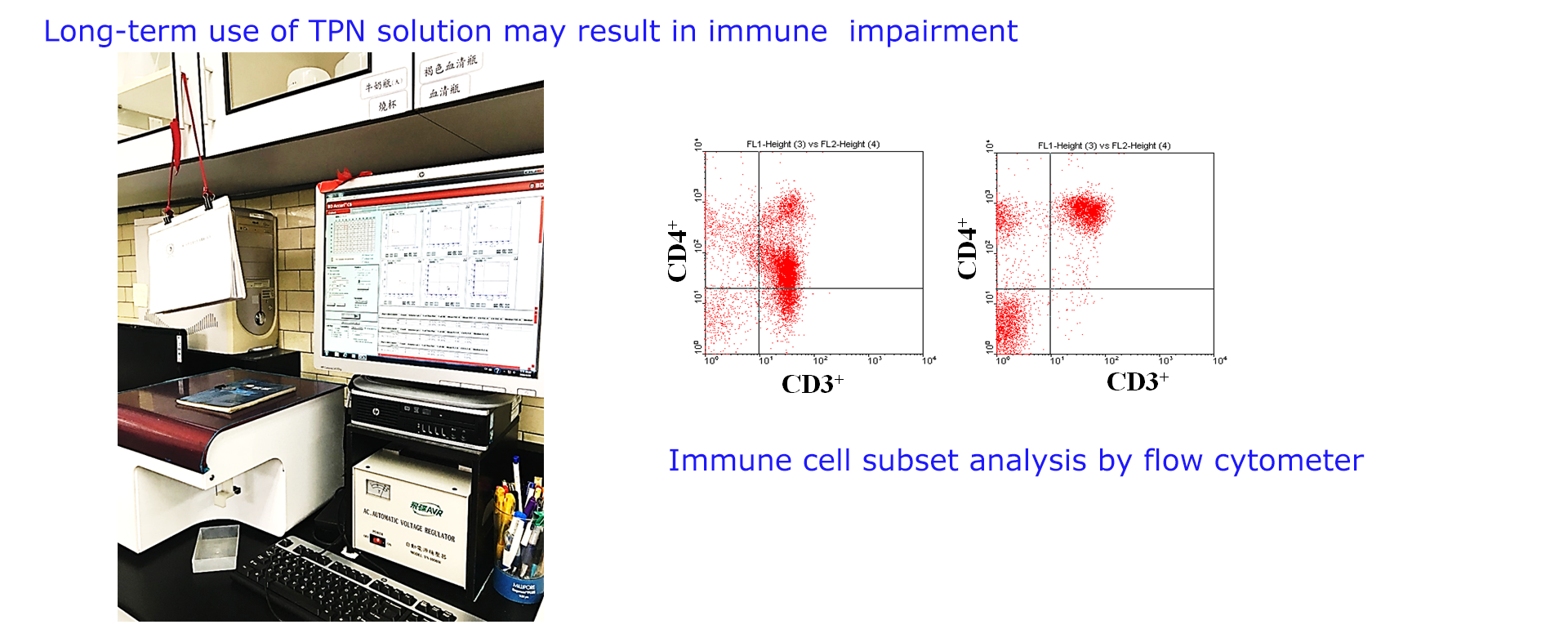
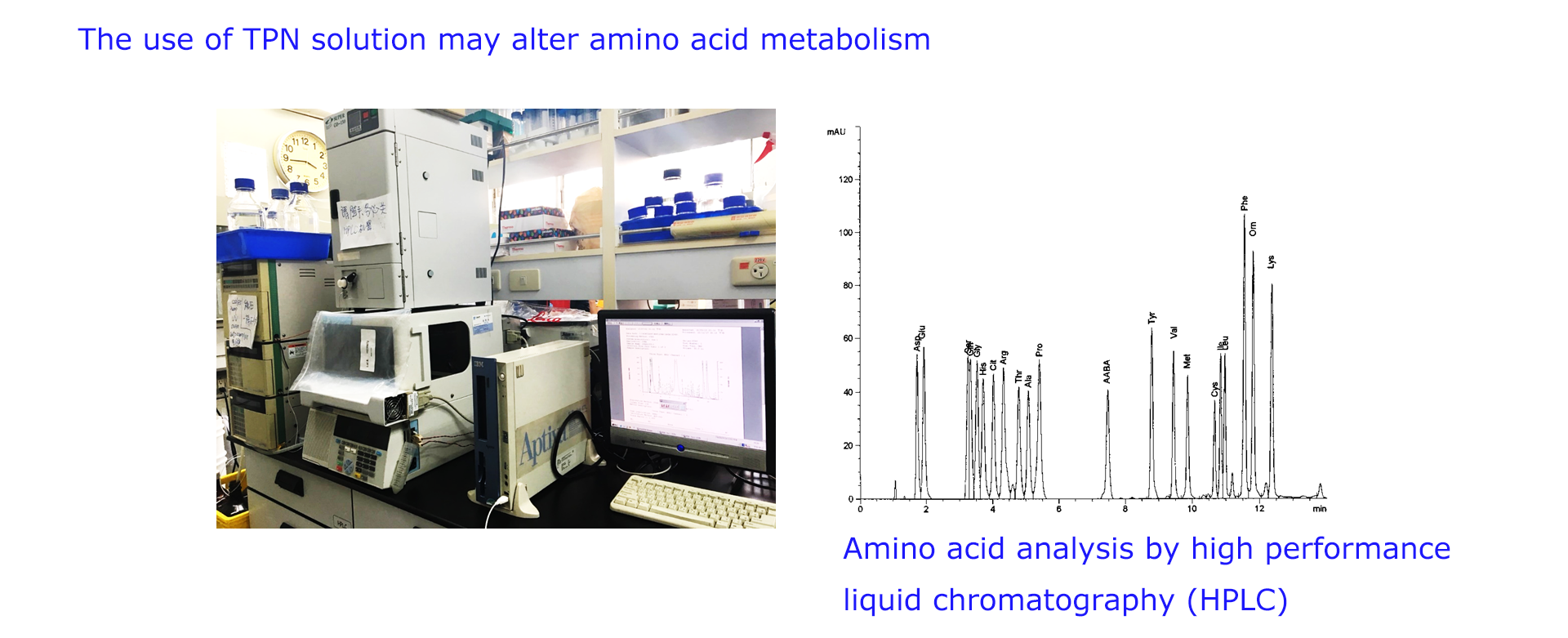
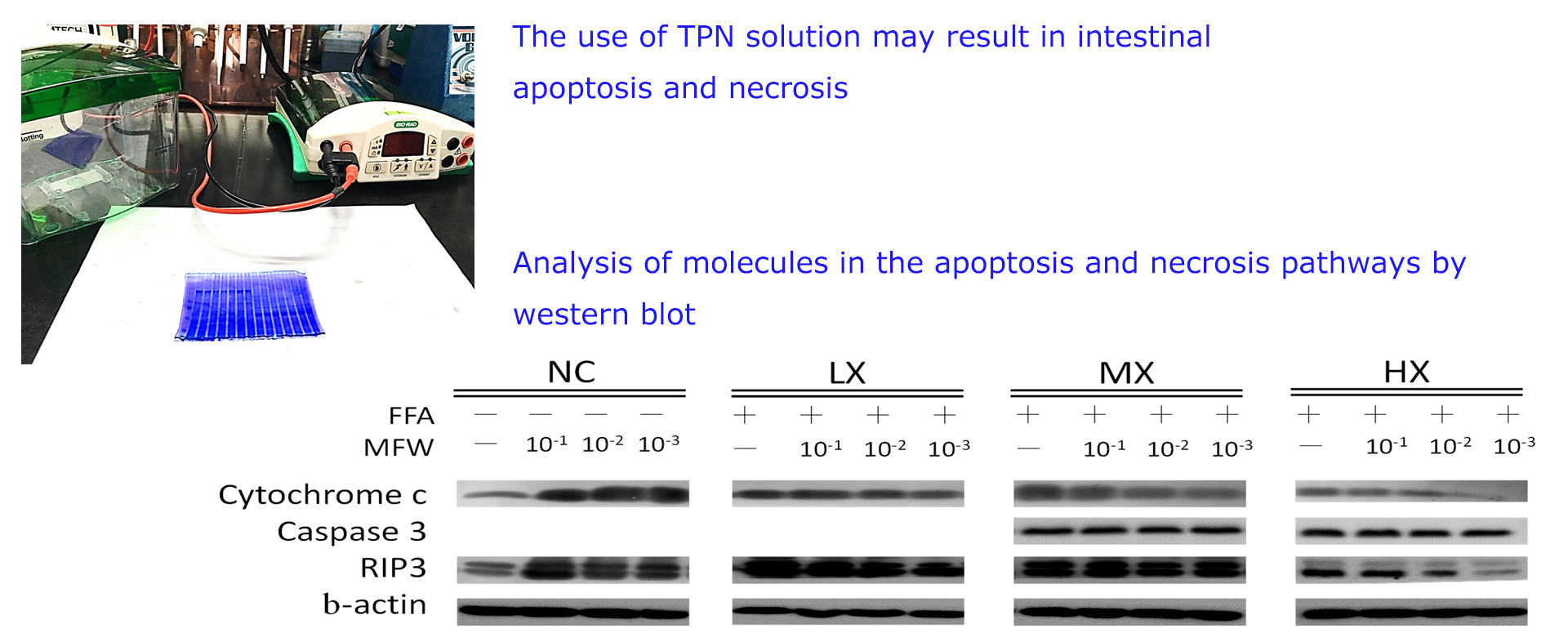
These TPN-induced hepatic abnormalities associated with increased oxidative stress and decreased antioxidant defenses. In addition, the lack of enteral nutrition result in gut atrophy which results in impaired immunity as the gut is the largest immune organ in the body. Consequently, several different immunonutrients and antioxidants, such as glutamine, arginine, n-3 fatty acids, and vitamin C and E, became regular supplements in TPN solutions for clinical use.
Using a rat model with different intestinal disorders, inflammation and hypermetabolic conditions, we have investigated the effects of arginine-metabolism associated amino acids, fish oil, antioxidants, and mushroom fermentation products on the metabolism, oxidative stress and immune responses. The molecular mechanisms of these adjuvants and nutraceuticals were also investigated. Our goal is to develop a clinically valuable and safer nutrition therapy to improve the intestinal function, nutrition status, clinical outcome, and life quality for patients with TPN support.
90 views