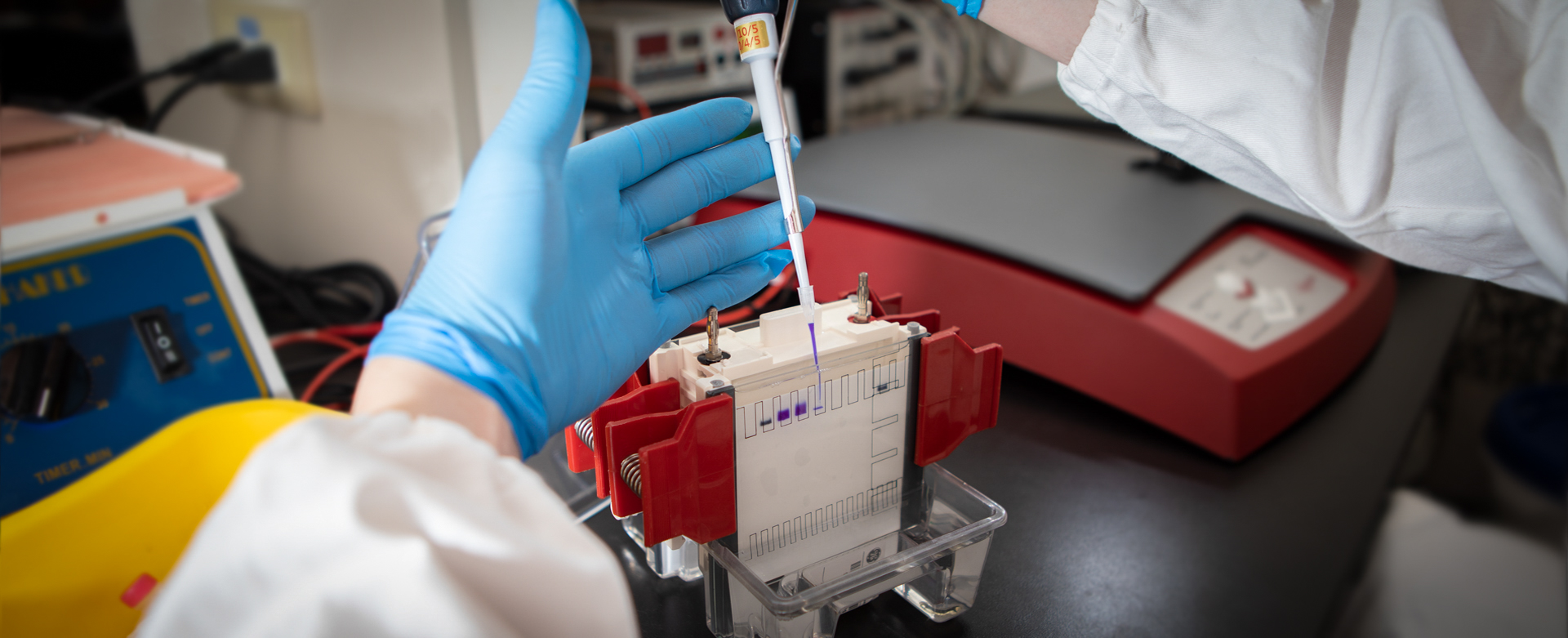
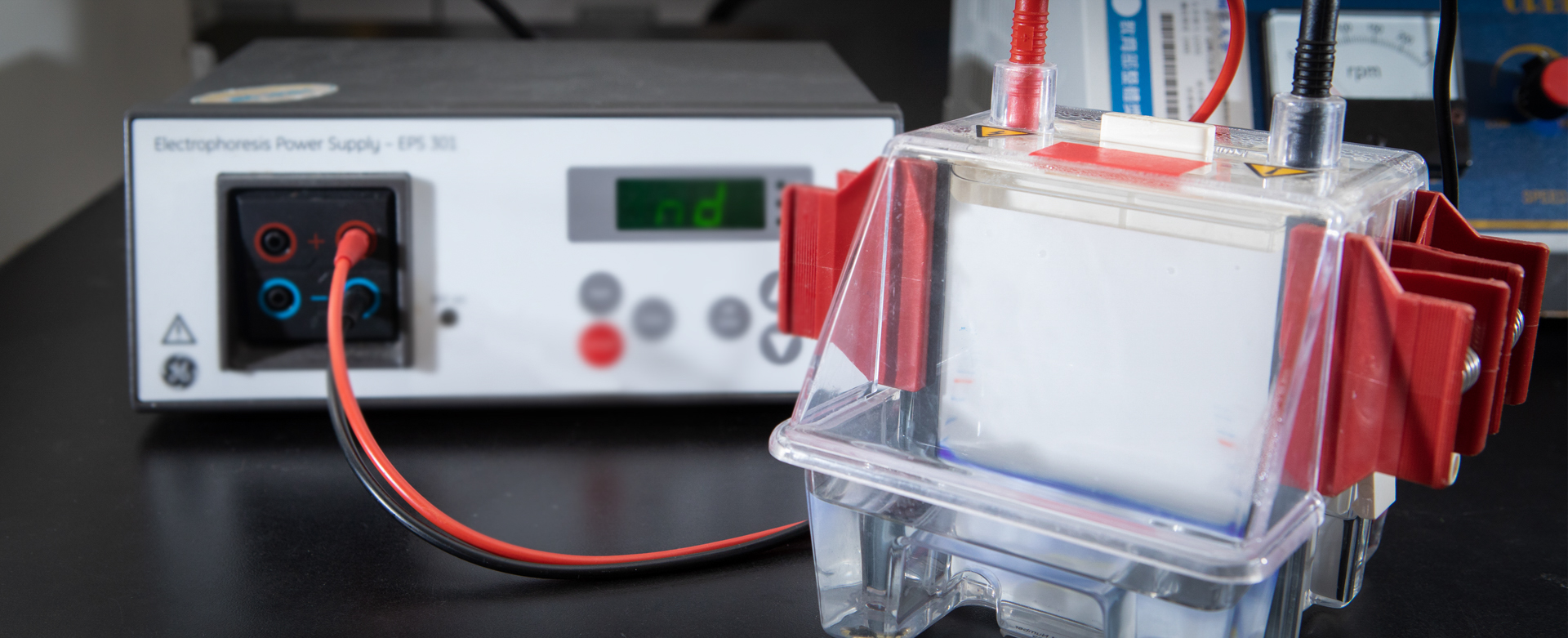
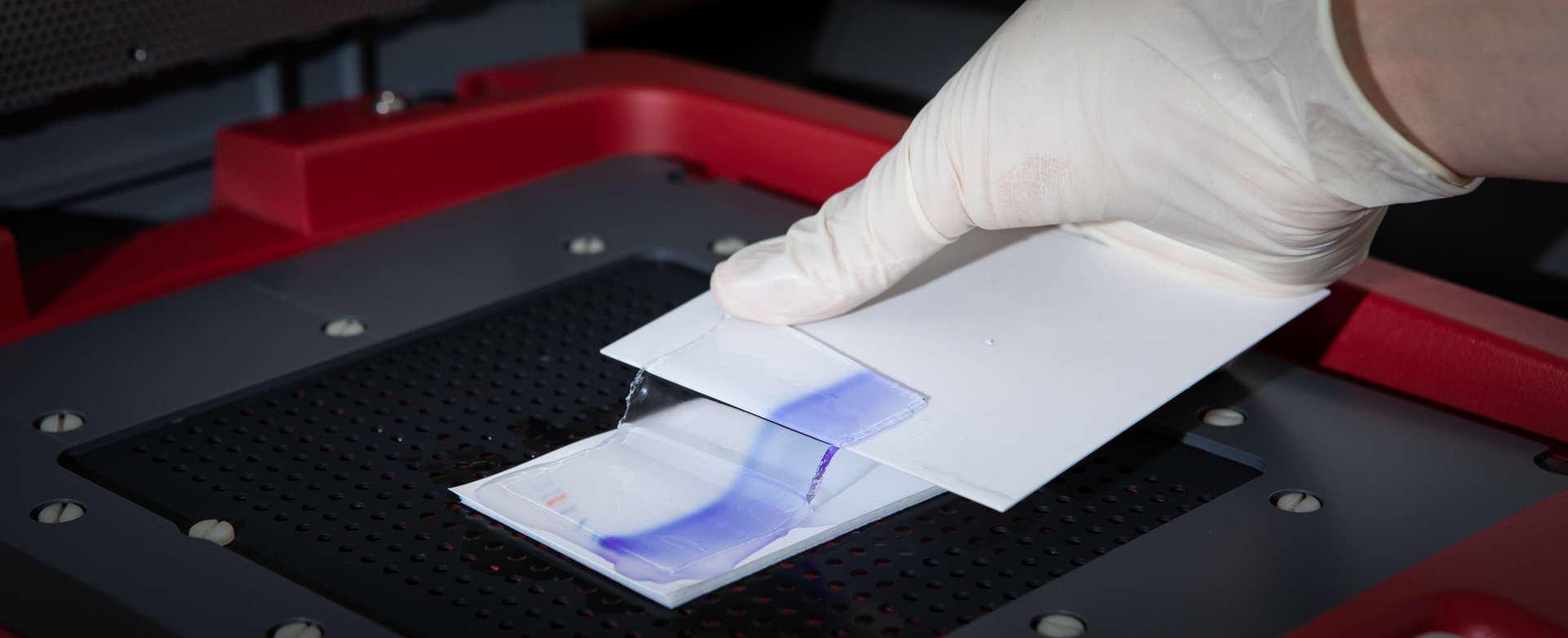
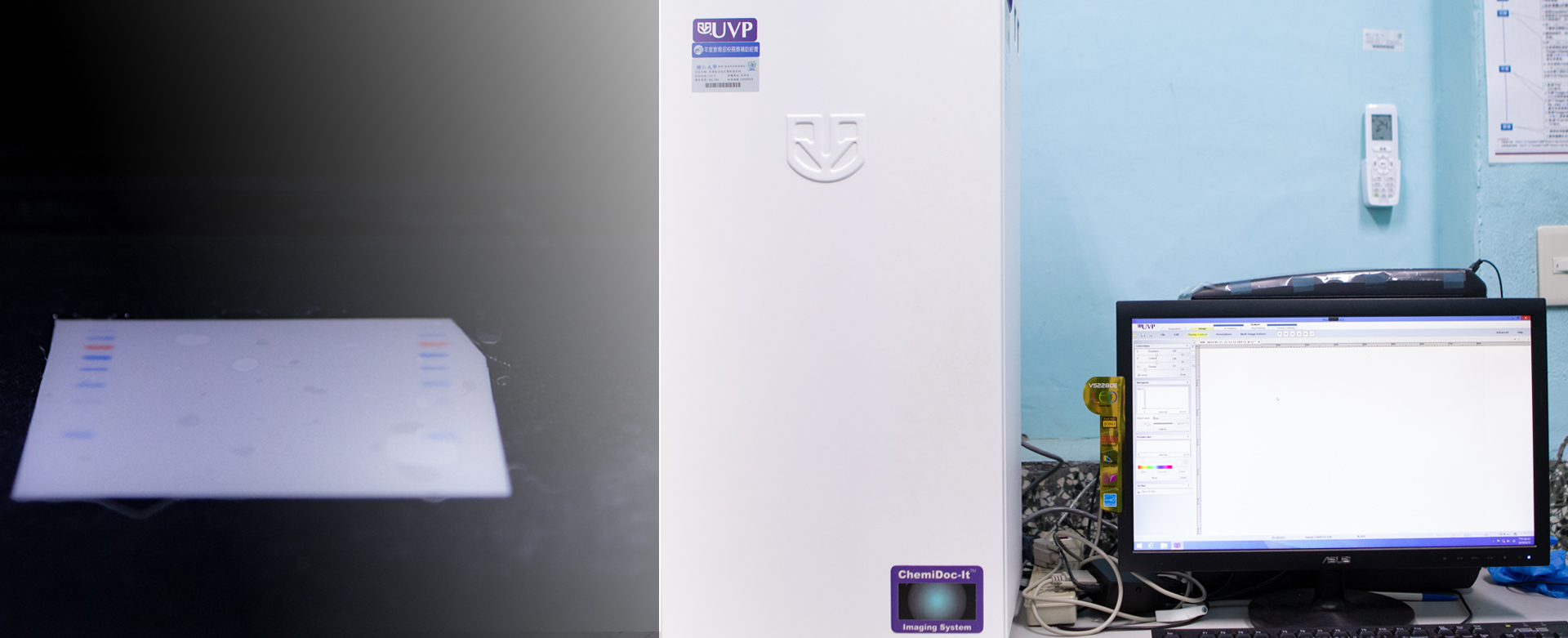
The pharmaceutical molecular target for clinical treatments
The pharmaceutical molecular target for cardiovascular diseases treatments.
Studies have shown that atherosclerosis is strongly associated with inflammation. C-reactive protein (CRP) is a key indicator of inflammation and is also thought to play an important role in the progression of atherosclerosis. This laboratory investigated the discovery that CRP can cause the transmission of inflammatory signals through the CD32 receptor and increase of endothelial cell adhesion factors. The Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta (PPARδ) agonist PPARδ agonist inhibits CRP receptor CD32 expression in endothelial cells more effectively than PPARγ agonists. It only requires one-tenth of the dose of the PPARγ agonist to achieve the same effect. This study demonstrated that PPAR The regulation of δ agonists in cardiovascular-related diseases would be a potential development potential. In addition, this laboratory has conducted more in-depth studies on the effects of PPAR delta agonists in the course of other diseases. In cardiomyocyte experiments, it was found that PPAR δ agonists can effectively reduce the CRP-induced cardiomyocyte inflammatory response through the message transmission of p38MAPK and JNK.
This study established that PPAR delta has a more potent inhibitory effect on the development of atherosclerosis than the drug PPAR gamma that has been used for many years. Help PPAR delta develop into a new atherosclerosis prevention drug.
The beneficial effects of Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta agonist by inhibiting receptor advanced glycation end-products in diabetic complications
As recent studies have shown that cardiovascular disease is more difficult to control in cardiovascular patients due to the stimulation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in patients with diabetes, and the number of people with diabetes worldwide increases year by year. Advanced glycation end products (AGEs), receptor to AGE (RAGE), are considered as the main cause of various complications of diabetes. Diabetic wound ulcers, diabetic nephropathy and diabetic cardiomyopathy. It will seriously affect the patient's quality of life, but also directly cause a lot of economic losses on medical care. At present, the physiopathological mechanism of these complications still needs to be studied more clearly, and the development in treatment and control is also urgently needed in the world today.
Research to control cardiovascular disease caused by AGE becomes even more urgent. The first use of human renal interstitial cells, the laboratory confirmed PPAR δ agonist can also be effective in inhibiting AGE-induced inflammatory response, and compared with the commonly used antioxidant EGCG effect difference. The effect on diabetic nephropathy further convinced us that PPAR δ agonists play a regulatory role in diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Therapeutic functional effects of gold nanoparticle with epigallocatechin and alpha lipoic acid
I have now confirmed by a series of experimental studies that my world's first antioxidant formula (patent replies: topical pharmaceutical dosage forms and their manufacturing methods) can effectively accelerate the healing of diabetic wounds through anti-inflammatory, RAGE and angiogenesis regulation. In addition, to further improve the bioavailability of this unique anti-oxidant formulation, I further found that the use of gas delivery mode to achieve better results, the invention is even more valuable clinical value of this formula. The results of this series of wound healing research have also received international attention. They were invited to organize their unique insights in the first 7% of the Journal in the field of pharmacology and have sought cooperation from Swiss manufacturers.
Recent application of nanotechnology in the treatment of diseases, the choice of 3-5nm nano-gold made of the physical application of animal models of wound healing in mice found that nano-gold can effectively assist the percutaneous absorption of antioxidants and reduce inflammation of the wound Response in this study and to explore the effect of nanogold on wound healing angiogenesis.
135 views