Featured Scientist

Author published in"Biochem Pharmacol"affiliate to
School of Medicine, College of Medicine,
Fu Jen Catholic University, New Taipei City, Taiwan
Article published in
"Biochem Pharmaco" Volume 175, May 2020, Article number 113928
New insights into the IL-12 and IL-23: From a molecular basis to clinical application in immune-mediated inflammation and cancers
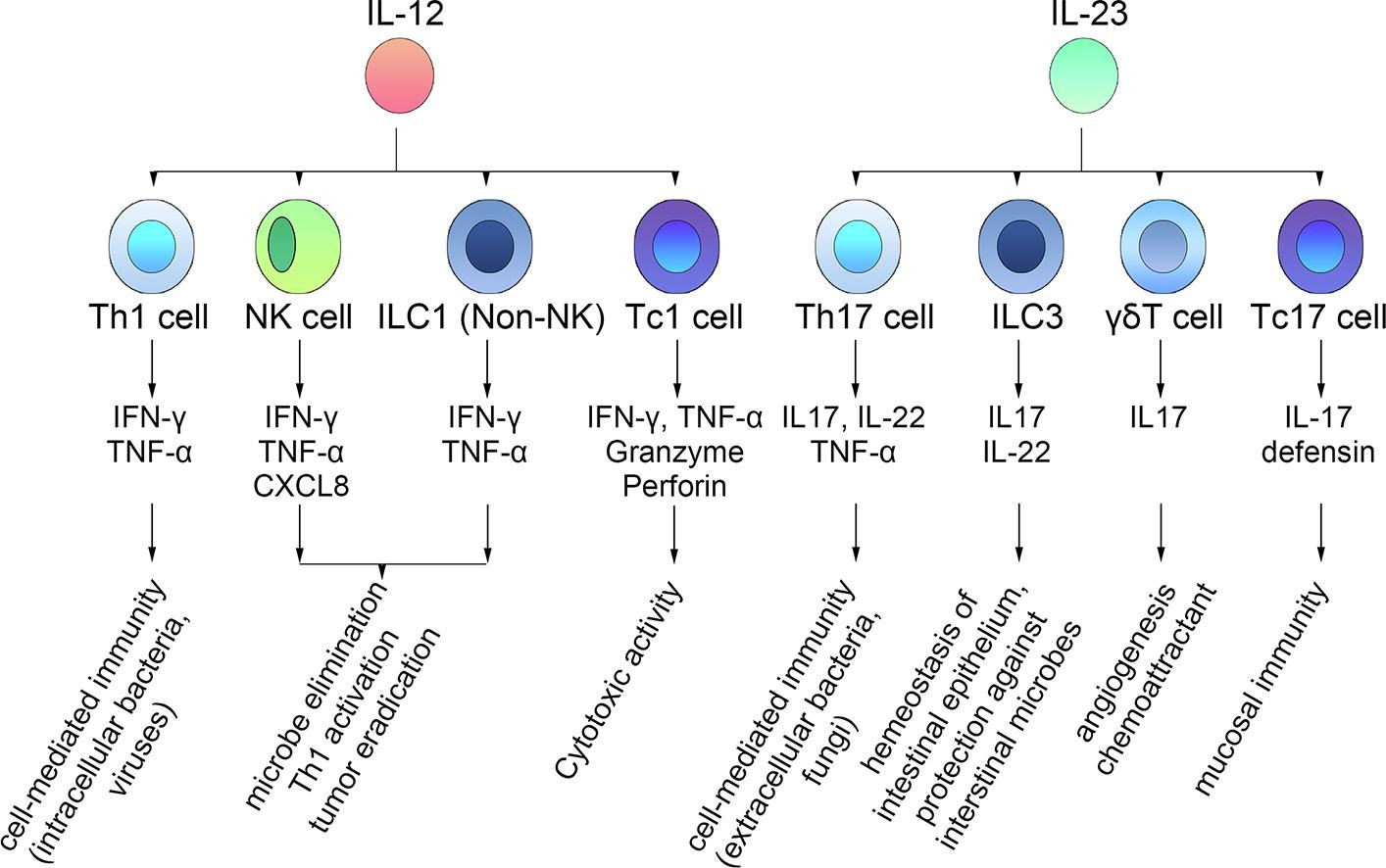
The cytokines interleukin-12 (IL-12) and IL-23 share a common IL-12/IL-23p40 subunit in structure and play a central role in T cell-mediated responses in inflammation. Over-activated IL-12 and IL-23 signaling drives aberrant T helper (Th) 1 and Th17 immune responses and contributes to immune-mediated diseases. Evidence from genome-wide association studies has shown that genetic alterations in the IL-12/IL-23 signaling pathways have significant links with chronic inflammation. In addition, accumulating evidence from animal models and clinical trials has provided insights into the effectiveness of blocking the IL-12/IL-23 pathways in immune regulation, broadening the clinical indications of IL-12/IL-23 pathway effectors in immune-mediated diseases. More recently, it has been addressed that the balance between IL and 12 and IL-23 is also critical in carcinogenesis. IL-12- and IL-23-driven T cell cytokines are especially important in controlling tumor initiation, growth, and metastasis, and thus, the IL-12/IL-23 pathway may be a promising target for immunotherapy. This review focuses on IL-12/IL-23 signal transduction and biological functionality in autoimmunity and oncoimmunology. We discuss the therapeutic rationale for targeting these cytokines to treat immune-mediated diseases and issues regarding their inadvertent consequences in the balance of host defense and tumor surveillance and summarize their recent clinical applications in immune-mediated diseases.
Keywords: Interleukin-12,Interleukin-23, AutoimmunityInnate cells,Cancer
89 views