Featured Scientist

Jung-Feng Hsieh, Ph.D.
Professor
Natural Products Chemistry
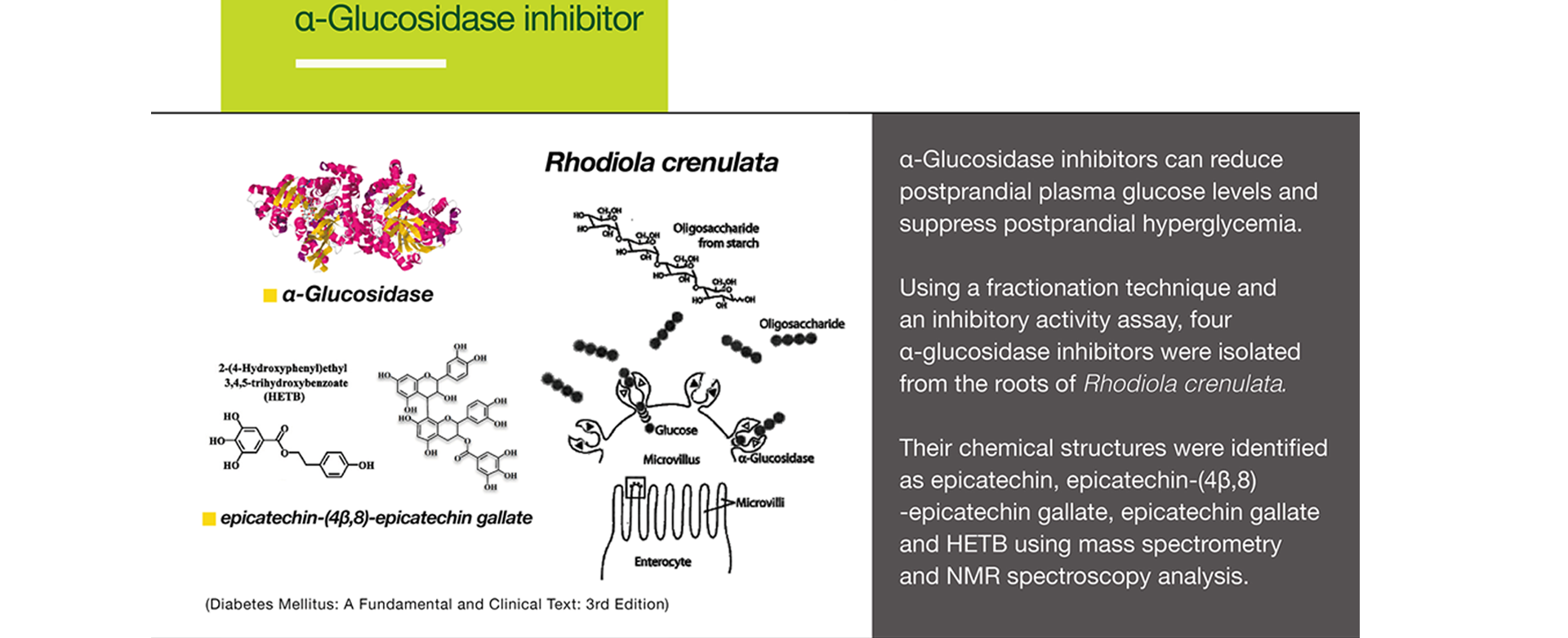
α-Glucosidase inhibitors can reduce postprandial plasma glucose levels and suppress postprandial hyperglycemia.
Using a fractionation technique and an inhibitory activity assay, four α-glucosidase inhibitors were isolated from the roots of Rhodiola crenulata.
Their chemical structures were identified as epicatechin, epicatechin-(4β,8)-epicatechin gallate, epicatechin gallate and HETB using mass spectrometry and NMR spectroscopy analysis.
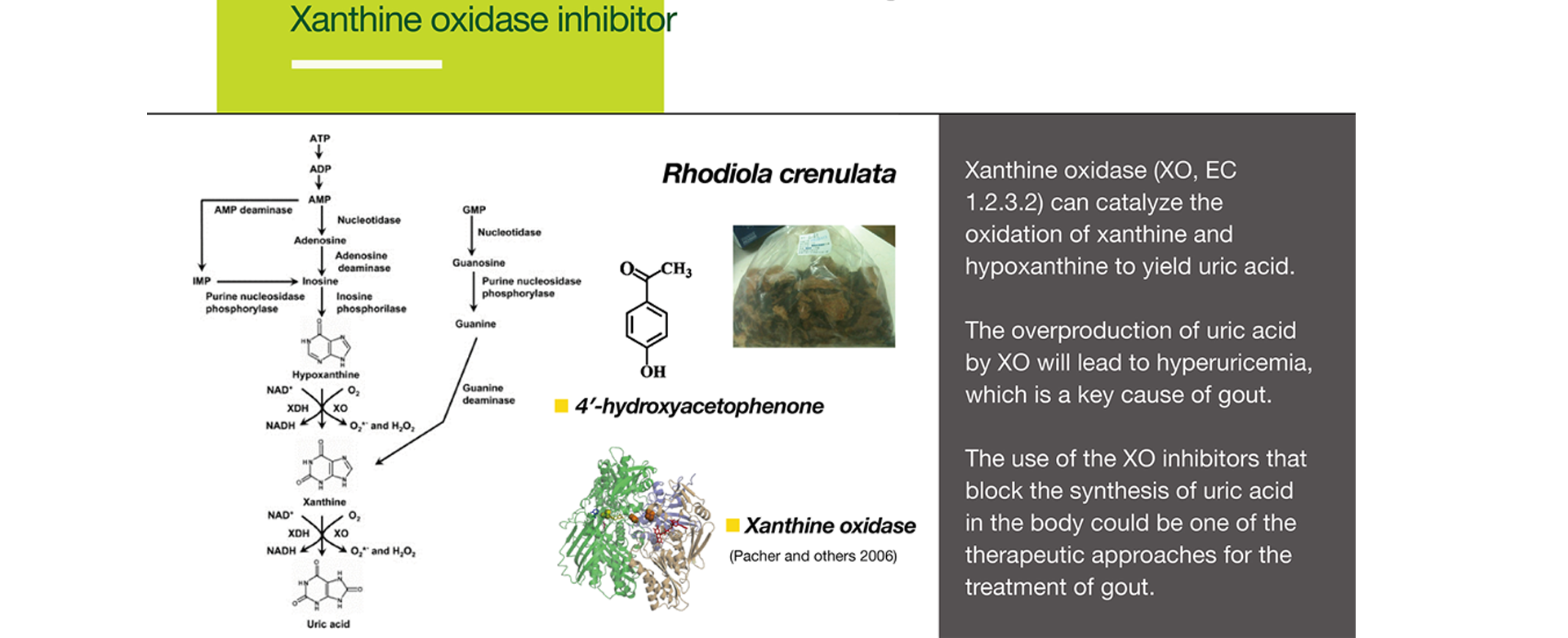
Xanthine oxidase (XO, EC1.2.3.2) can catalyze the oxidation of xanthine and hypoxanthine to yield uric acid.
The overproduction of uric acid by XO will lead to hyperuricemia, which is a key cause of gout.
The use of the XO inhibitors that block the synthesis of uric acid in the body could be one of the therapeutic approaches for the treatment of gout.
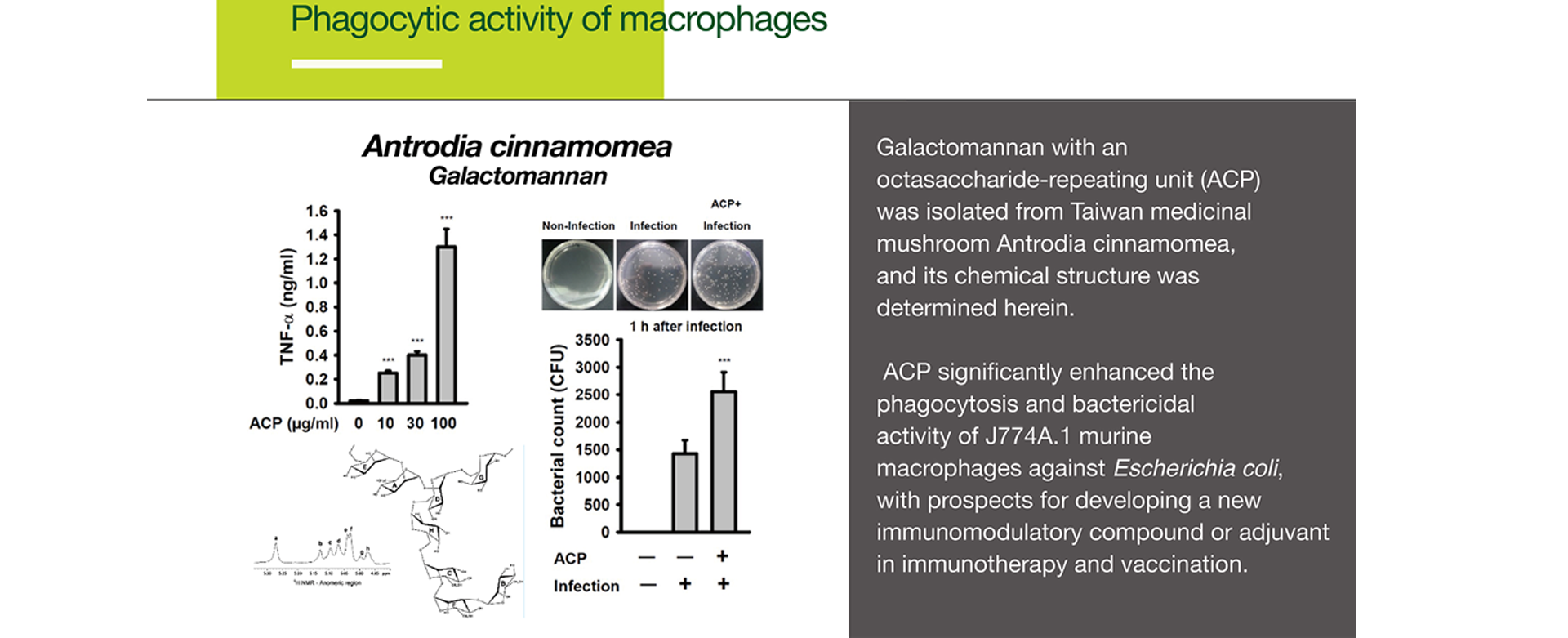
Galactomannan with an octasaccharide-repeating unit (ACP) was isolated from Taiwan medicinal mushroom Antrodia cinnamomea, and its chemical structure was determined herein.
ACP significantly enhanced the phagocytosis and bactericidal activity of J774A.1 murine macrophages against Escherichia coli, with prospects for developing a new immunomodulatory compound or adjuvant in immunotherapy and vaccination.
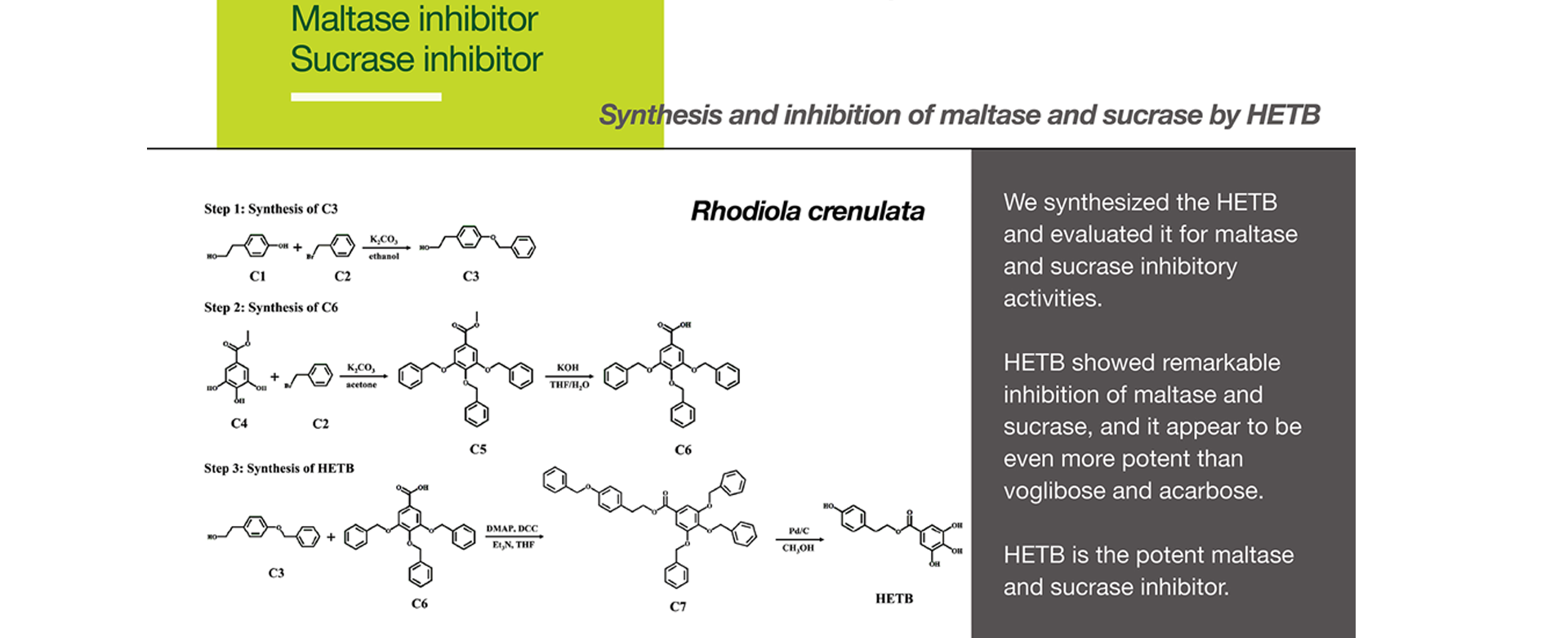
We synthesized the HETB and evaluated it for maltase and sucrase inhibitory activities.
HETB showed remarkable inhibition of maltase and sucrase, and it appear to be even more potent than voglibose and acarbose.
HELB is the potent maltase and sucrase inhibitor.
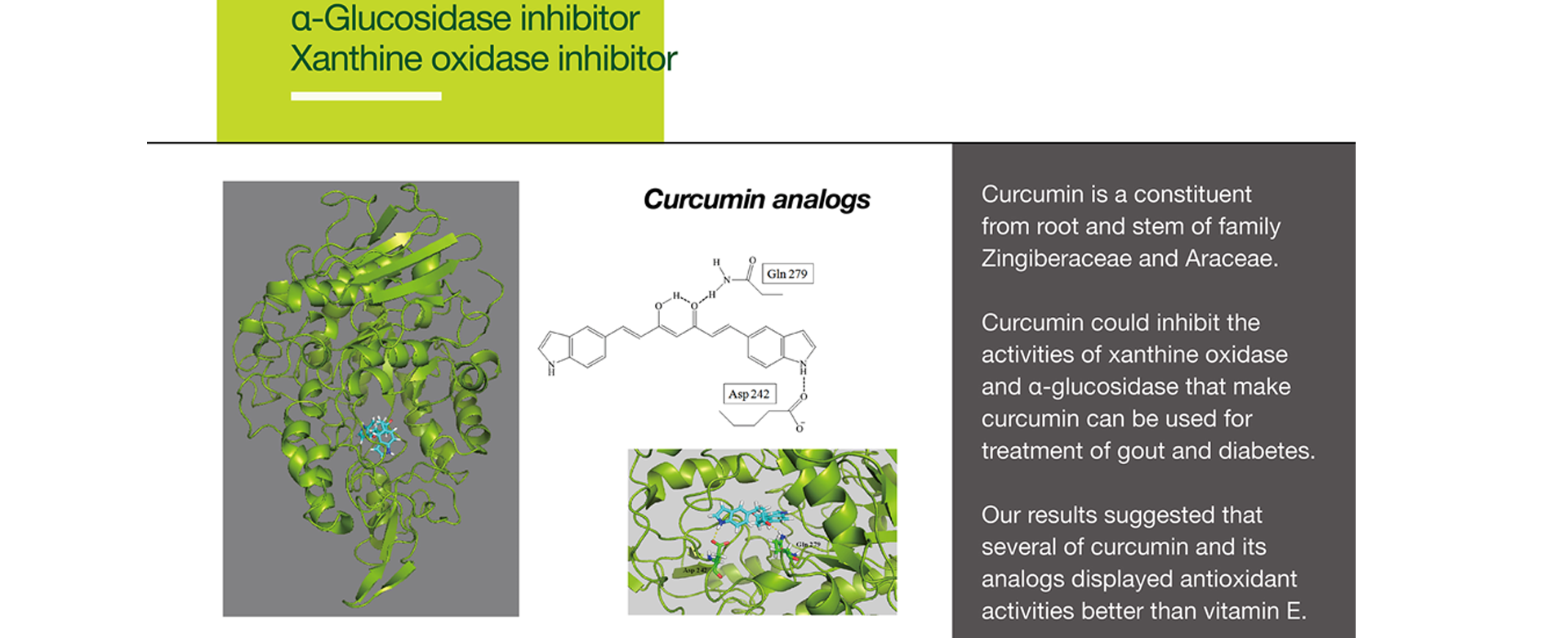
Curcumin is a constituent from root and stem of family Zingiberaceae and Araceae.
Curcumin could inhibit the activities of xanthine oxidase and α-glucosidase that make curcumin can be used for treatment of gout and diabetes.
Our results suggested that several of curcumin and its analogs displayed antioxidant activities better than vitamin E.
73 views