Featured Scientist

Author published in"Journal of Ethnopharmacology"affiliate to
MS Program Transdisciplinary Long Term Care,
Fu Jen Catholic University, New Taipei City, Taiwan
Article published in
"Journal of Ethnopharmacology" Volume 263, 5 December 2020, 113037
An isoflavone extract from soybean cake suppresses 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced contact dermatitis
Ethnopharmacological relevance
Numerous epidemiological and clinical studies have demonstrated the protective role of dietary isoflavones against development of several chronic diseases. ISO-1, one fraction of isoflavone powders derived from soybean cake, is reported to attenuate inflammation and photodamage.
Aim of the study
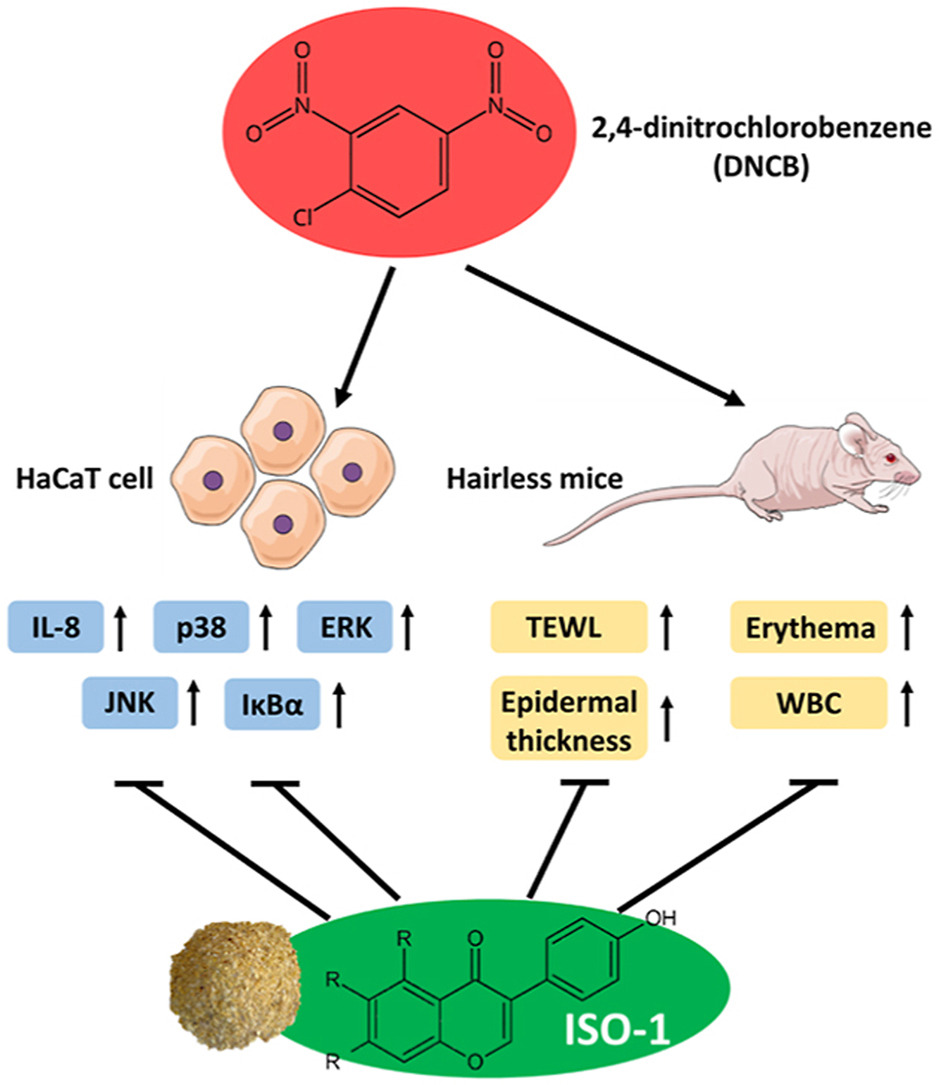
Contact dermatitis is a common inflammatory skin disease, which accounts for most occupational skin disorders. Instead of oral administration, we aimed to explore the effects of topical ISO-1 application on contact dermatitis by using 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB)-stimulated HaCaT keratinocytes and DNCB-induced mouse dermatitis as models.
Materials and methods
In the in vitro study, we first evaluated the biologic effects of DNCB on HaCaT keratinocytes. HaCaT keratinocytes were treated with 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB), and cell viability was measured by MTT assay. Then, we detect the prominent induction of IL-8 mRNA expression after DNCB and ISO-1 treatment by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), and release of IL-8 from HaCaT keratinocytes was measured by ELISA assay. HaCaT keratinocytes were pretreated with ISO-1 and then treated with DNCB, phosphorylation of JNK, p38, ERK and IκBα was analyzed by western blot. In the in vivo study, the hairless mice were used for an induced contact dermatitis model. The surface changes in the dorsal skin after DNCB and ISO-1 treatment were recorded using photography, and TEWL, erythema were measured using an MPA-580 cutometer. Blood was also collected from mice for measurement of white blood cell counts.
Results
Results showed ISO-1 inhibited DNCB-induced IL-8 production and also suppressed DNCB-induced phosphorylation of JNK and p38, and IκBα in HaCaT. In the animal model of DNCB-induced contact dermatitis, topical ISO-1 treatment significantly decreased DNCB-induced erythema and transepidermal water loss (TEWL) in mouse skin. ISO-1 also reduced DNCB-induced skin thickening and increase of white blood cell count.
Conclusions
ISO-1 is promising for improvement of DNCB-induced inflammation and skin barrier impairment, suggesting the potential application of topical ISO-1 for inflammatory dermatoses. [Full article]
Keywords Abbreviations 1. Introduction 2. Materials and methods 3. Results 4. Discussion 5. Conclusion
52 views