Featured Scientist

Author published in"International Journal of Biological Macromolecules"affiliate to
Department of Food Science,
Fu Jen Catholic University, New Taipei City, Taiwan
Article publish in
"International Journal of Biological Macromolecules" Volume 161, 15 October 2020, Pages 1484-1495
Green synthesis, characterization and evaluation of catalytic and antibacterial activities of chitosan, glycol chitosan and poly(γ-glutamic acid) capped gold nanoparticles
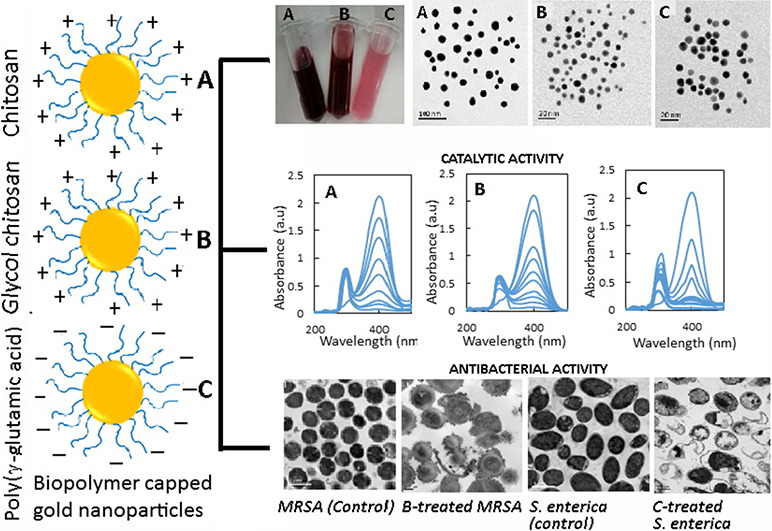
Gold nanoparticles capped with chitosan (CH-NGs), glycol chitosan (GC-NGs) and poly(γ-glutamic acid) (PA-NGs) were synthesized separately, characterized and evaluated for catalytic and antibacterial activities. Surface Plasmon resonance peak at 520–530 nm confirmed the formation of NGs, while FTIR spectra revealed the involvement of hydroxyl, amine and amide groups in biopolymers on NGs formation and coating. Particle size, zeta potential and surface coating were respectively 21.7 nm, +50.2 mV and 20% for CH-NGs, 5.6 nm, +46.5 mV and 43.5% for GC-NGs and 7.4 nm, −37.3 mV and 34.5% for PA-NGs. Compared to citrate-capped NGs (CT-NGs), biopolymer-capped NGs exhibited high catalytic activity in a 4-nitrophenol reduction model with the pseudo first-order catalytic rate for PA-NGs being 4–6 fold higher than CH-NGs and GC-NGs. No significant antibacterial effect was shown for CT-NGs. However, PA-NGs was superior to gentamycin in inhibiting Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli-O157:H7, while CH-NGs and GC-NGs showed the highest antibacterial effect against Listeria monocytogenes, followed by Salmonella enterica, Escherichia coli-O157:H7, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Staphylococcus aureus. TEM images showed that GC-NGs were attached on MRSA surface to alter cell permeability, block nutrient flow and disrupt cell membrane, whereas PA-NGs penetrated into Salmonella enterica to generate cavities, plasmolysis and disintegration.[Full article]
Keywords: Gold nanoparticles Poly(γ-glutamic acid) ChitosanGlycol chitosan Catalytic activity Antibacterial activity
41 views