Featured Scientist

Ming-chih Chen
Chen, Ming-Chih
University Distinguished Research Professor & Dean of Research and Development
Education:Ph. D., Industrial Engineering, Texas A&M University, U.S.A.
Specialties:Production and Operation Management, Total Quality Management
A framework to predict second primary lung cancer patients by using ensemble models
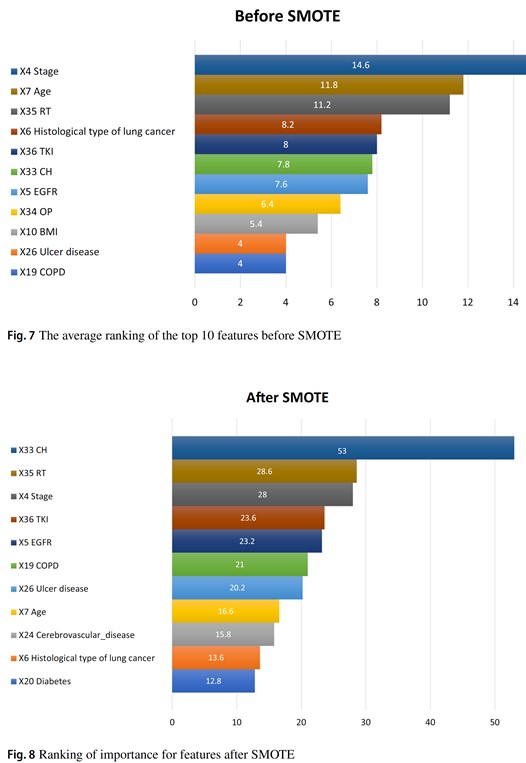
Machine learning (ML) model prediction, which has been wildly used in healthcare industry recently, serves as a tool to help users to make quick decisions. The prediction results could improve treatment outcomes and reduce the medical expenses. This research proposed the ML-based decision tool to predict the second primary lung cancer probability within lung cancer patients. This tool included following stages: The first stage is data processing to select the target patients by using National Health Insurance Research Database from 2011 to 2016 period as study. The second stage has used synthetic minority oversampling technique (SMOTE) to make data balancing. The third stage is feature selecting, and in final stage, we have applied five ML algorithms, which is included: Logistic Regression (LGR), Decision Tree, Random Forests (RF), multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS), and extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) with optimal features, then followed by building ensemble models. The results show that after feature selection, the ensemble models yield an accuracy rate 0.932. Different types of therapy (Chemotherapy (CH); Radiotherapy (RT), tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI)), different clinical stages, and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) states were the top five optimal features affecting developed second primary lung cancer. This study can help physicians to identify the possibility with second primary lung cancer patients and make complete treatment plans for them.
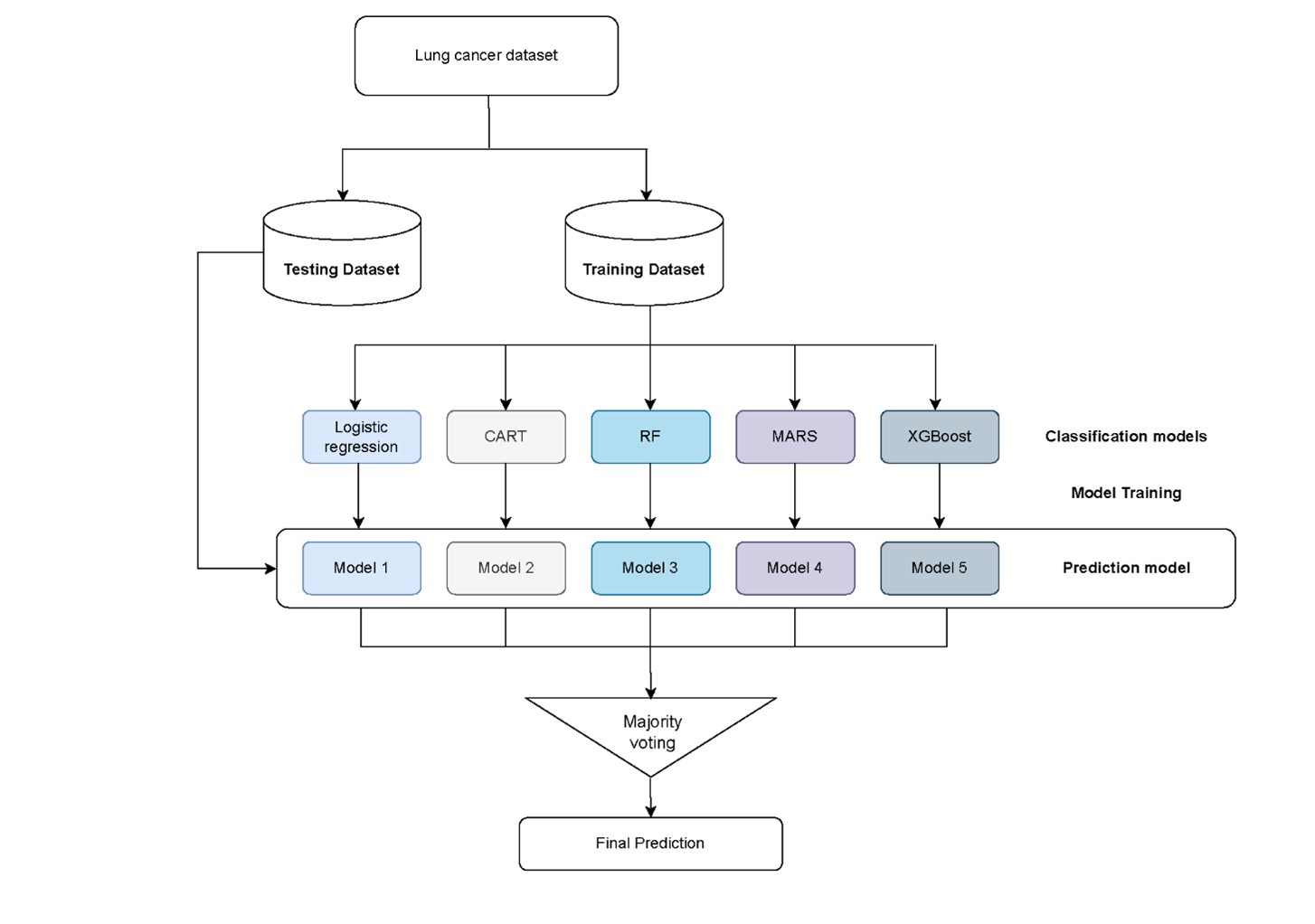
Fig. 3 The concept of majority voting ensemble modeling in this study