Featured Scientist

Jung-Feng Hsieh, Ph.D.
Professor
Effects of fluidized bed coating with carboxymethyl cellulose and pectin on the physicochemical properties of fermented black bean dregs
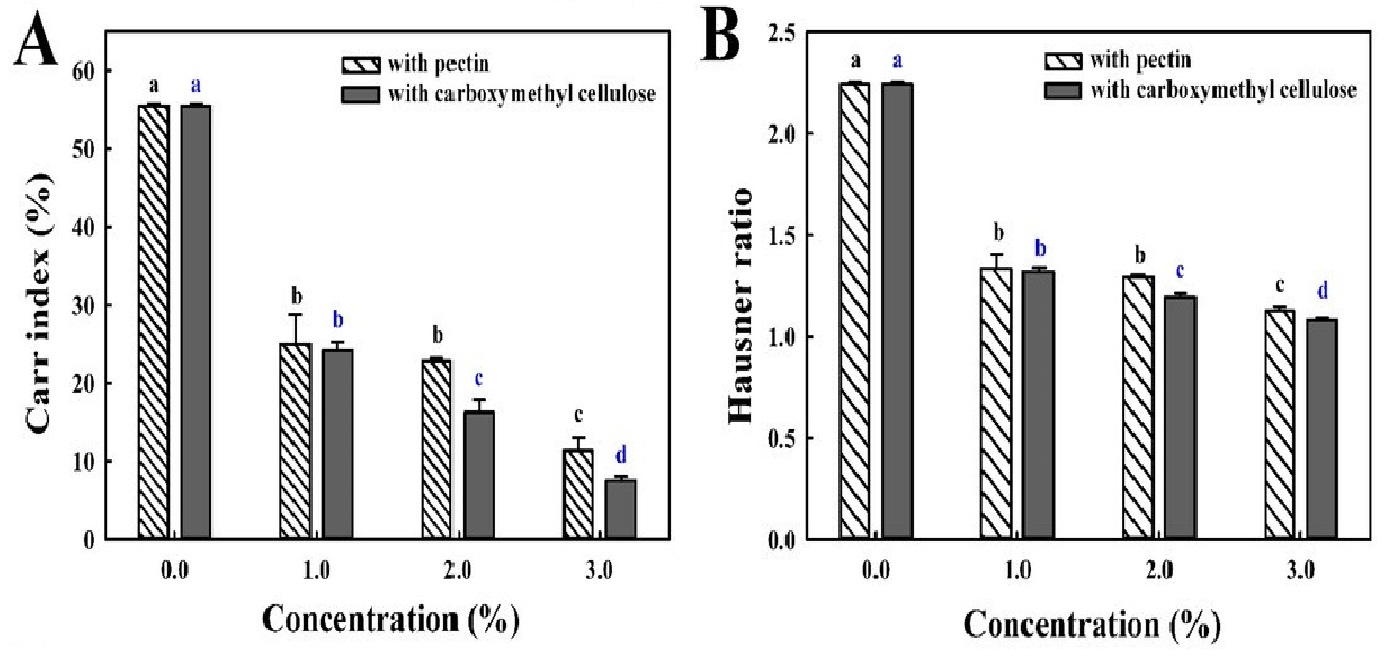
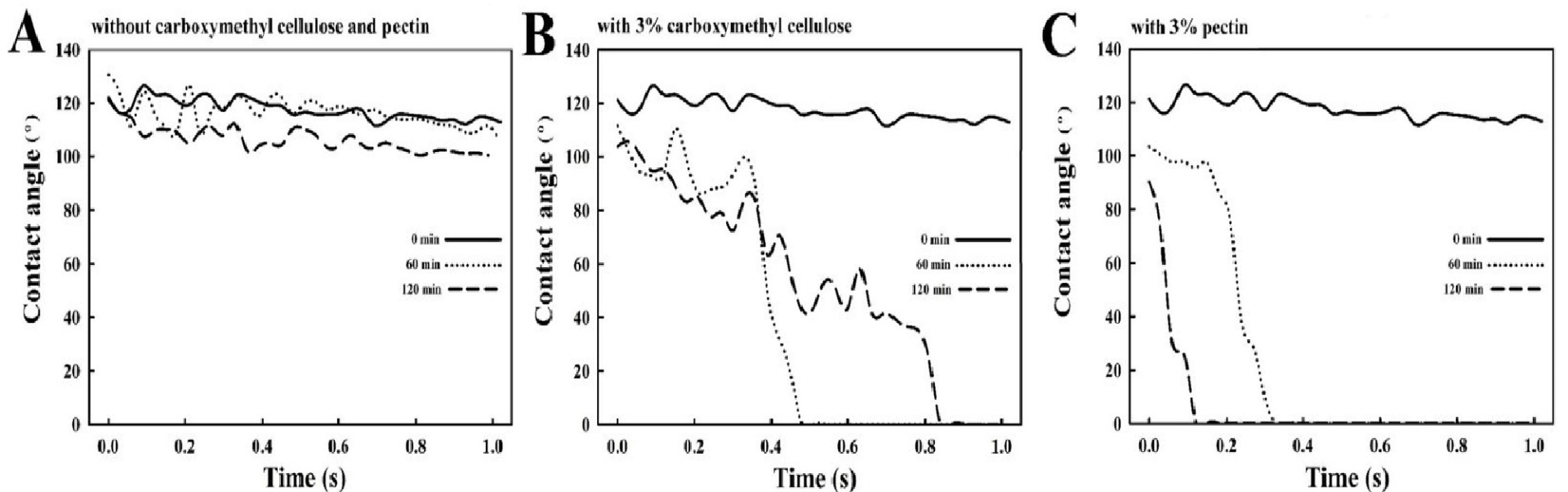
The changes in the physicochemical properties of fermented black bean dregs (FBBD) coated with carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) solution (0-3%) and pectin solution (0-3%) on a fluidized bed were analyzed. The Carr index of the FBBD powder decreased from 55.4 ± 0.3% to 7.5 ± 0.4% after coating with CMC solution (3%) and to 11.3 ± 1.6% after coating with pectin solution (3%) for 120 min. After coating with CMC solution (3%) for 120 min, the proportion of medium-sized particles decreased significantly with the increased duration of the coating process, whereas the proportion of large-sized particles increased. Microstructural analysis by scanning electron microscopy showed that the particle size significantly increased and the surface changed from rough to smooth. The L* and b* values of the powder samples decreased from 45.5 ± 0.1 and 17.2 ± 0.1 to 32.9 ± 0.2 and 15.3 ± 0.1, respectively, whereas the a* value increased from 7.6 ± 0.1 to 8.9 ± 0.1; thus, the sample color changed from bright to dark and tended toward bluish and reddish colors. The wettability and solubility of the powder samples increased significantly with the increased duration of the coating process, but the water-holding capacity decreased. Moreover, FBBD coated with pectin solution (3%) and CMC solution (3%) on a fluidized bed for 120 min exhibited similar physicochemical properties. Thus, FBBD powder exhibited favorable flowability, wettability, and solubility after 120 min of coating with CMC solution (3%) or pectin solution (3%).
Cheng Huang, Meng-I Kuo, Chun-Ping Lu, Bang-Yuan Chen, Chien-Cheng Yeh, Chia-I Chang, Cheng-Hsun Jao, Yi-Chung Lai, Jung-Feng Hsieh. 2025. Effects of fluidized bed coating with carboxymethyl cellulose and pectin on the physicochemical properties of fermented black bean dregs. Processes, 13(4): 1066.
Keywords:fluidized bed coating; carboxymethyl cellulose; pectin; fermented black bean dregs; powder flowability
4 views