Featured Scientist

Chi-Feng Hung, Ph.D.
Distinguished Professor
d-Limonene inhibits cytokines and chemokines expression by regulating NF-kappaB and STAT in HaCat cells and DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis in BALB/c mice
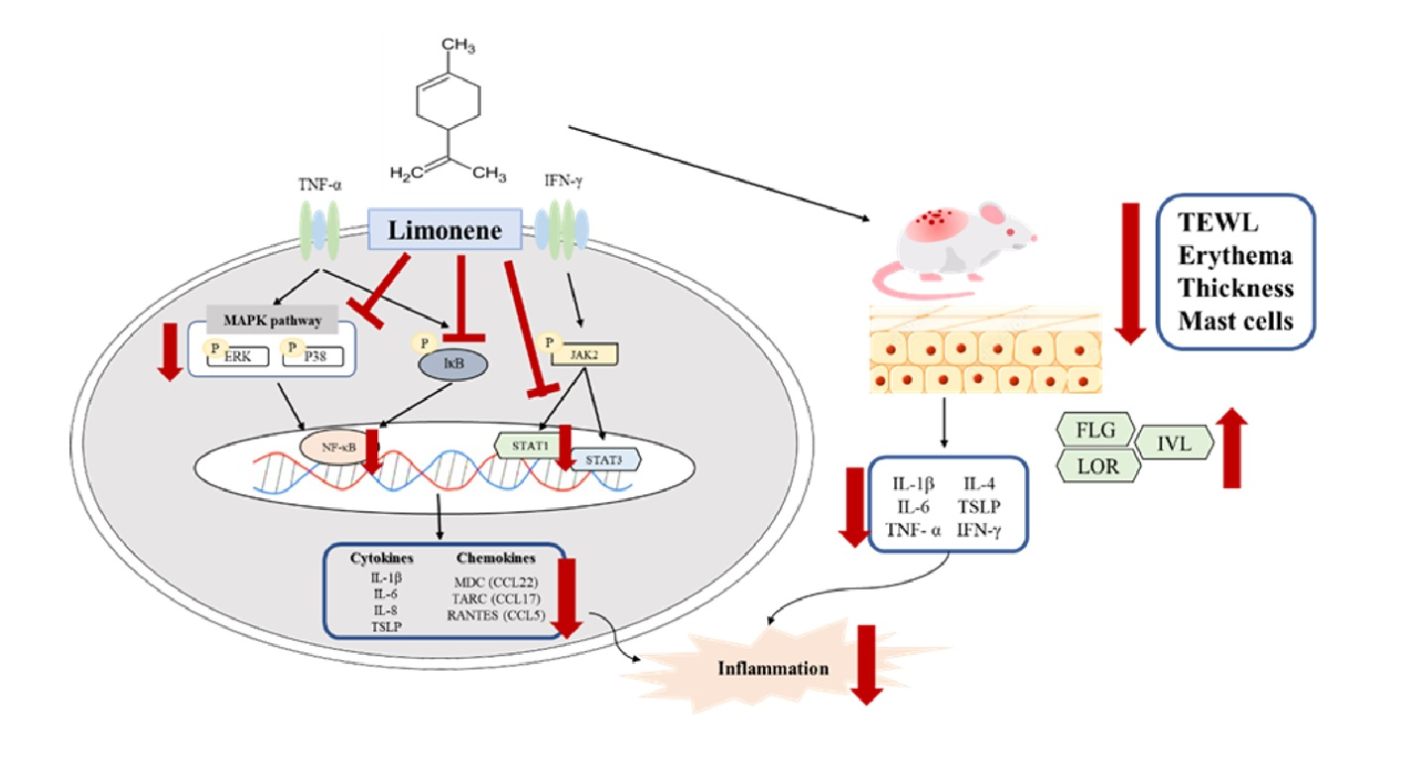
Background: Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic and persistent inflammatory skin disorder characterized by itching and redness. AD can occur at any age, significantly affecting patients' quality of life, and its prevalence is continuously increasing, making it a serious health problem. Relief of itching is considered a primary treatment goal for AD. However, treatment with steroids has side effects, such as thinning of the skin barrier. Therefore, more research is needed to develop safer treatments. Limonene is a naturally occurring monocyclic monoterpene widely used in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. It is present in citrus peel oil and is the main active compound. Various studies have found that limonene has multiple biological activities, including antioxidative, antidiabetic, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, antifibrotic, and antigenotoxic effects. Consequently, this study aims to explore whether limonene has a therapeutic effect on atopic dermatitis based on its anti-inflammatory potential.
Methods: In this study, we investigated the expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and chemokines, conducted histopathological analyses, and collected physiological data from BALB/c mice with atopic-like dermatitis induced by 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene and TNF-α/IFN-γ-stimulated HaCaT cells.
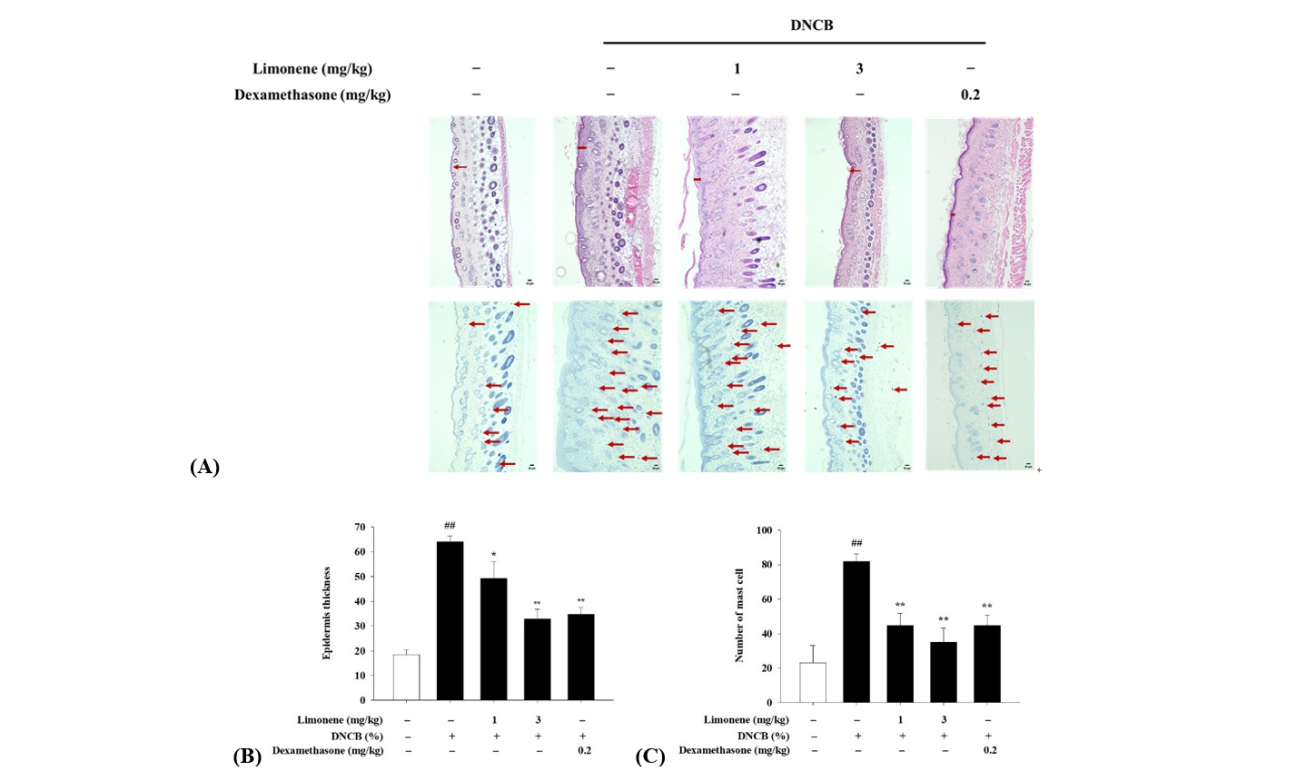
Results: In vitro studies have shown that limonene can inhibit the expression of cytokines and chemokines induced by TNF-α/IFN-γ stimulation of human keratinocytes (HaCat), and reduce the phosphorylation of the MAPK, NF-κB, and JAK/STAT signaling pathways. In vivo studies utilized a mouse model of atopic dermatitis induced by dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB). The results indicate that limonene can reduce DNCB-induced skin barrier damage and itching responses, as well as physiological parameters such as trans-epidermal water loss (TEWL), erythema, and ear thickness. Additionally, limonene can reduce the mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that the anti-inflammatory effect of limonene has therapeutic potential in the treatment of atopic dermatitis.
Keywords:limonene, atopic dermatitis, keratinocyte, MAPK, NF-κB, JAK/STAT
11 views