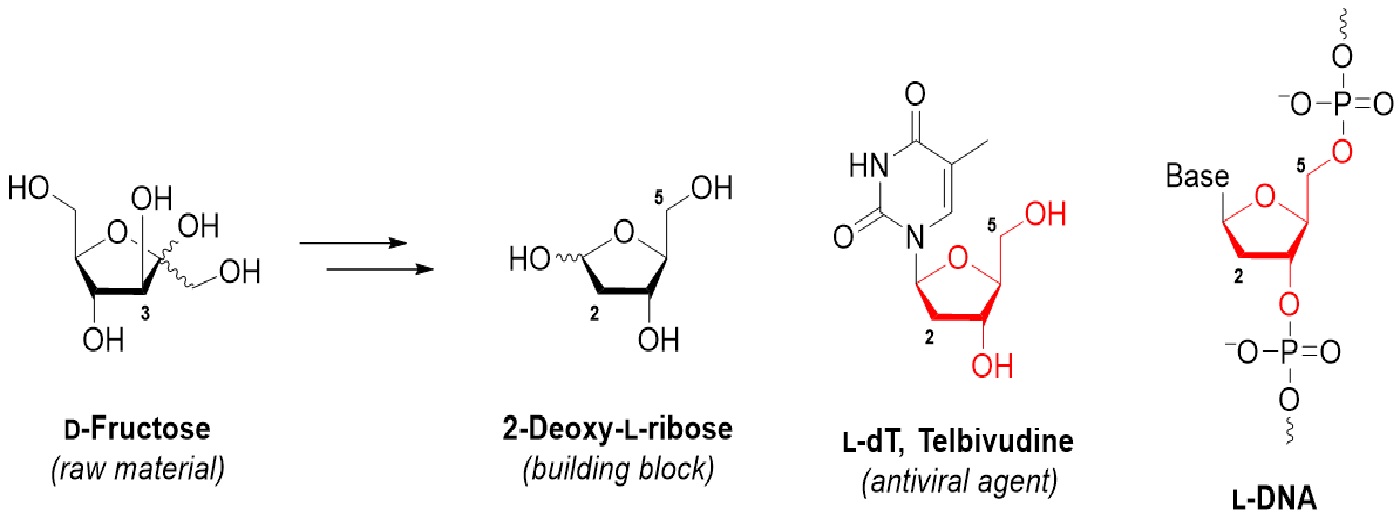
From a Carbohydrate Raw Material to an Important Building Block
The research developed a straightforward method for the conversion of a lowcost carbohydrate (D-fructose) into an important building block (2-deoxy-L-ribose). 2-Deoxy-L-ribose is used as the sugar component for synthesis of L-DNA, and various antiviral or anticancer drugs, such as L-dT. This synthetic methodology involved a carbonyl translocation process and a lipase hydrolysis reaction, which could be potentially applied in the pharmaceutical industry for the synthesis of 2-deoxy-L-ribose and its relative derivatives. So far as we know, this method uses the cheapest starting material and employs the shortest synthetic route for converting a D-sugar into 2-deoxy-L-ribose.
Keywords:raw material, antiviral agent, drug development
6 views