Featured Scientist

Su-Jane Wang, Ph.D.
Professor
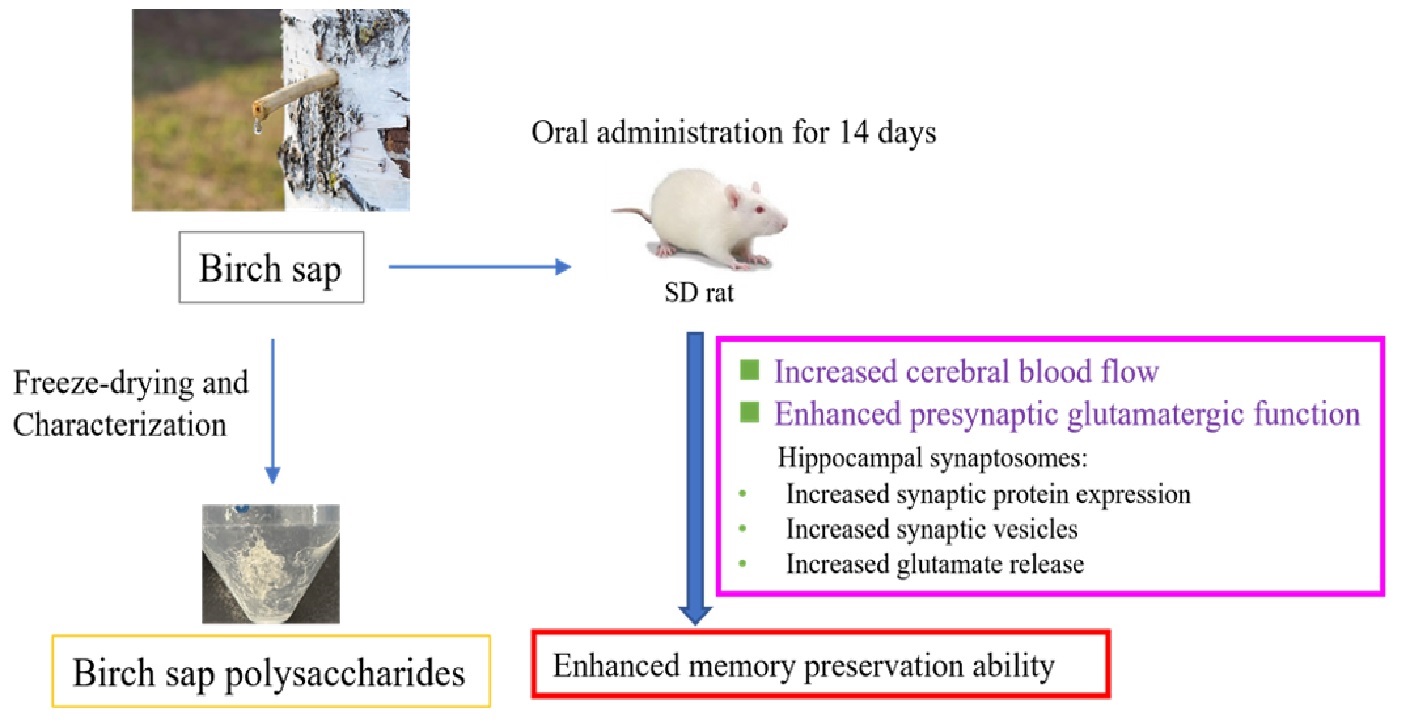
Birch sap preserves memory function in rats
The effect of oral administration of birch sap on memory may be due to an increased expression of synaptic proteins and a higher number of synaptic vesicles in the hippocampal nerve terminals, thereby enhancing glutamate release in the hippocampus of these rats. Additionally, memory preservation in the birch sap-treated rats may be associated with its modulatory effects on cerebral blood flow.
Keywords:birch sap; memory function; glutamate release; synaptic proteins; synaptosome; hippocampus
13 views