Featured Scientist

Chi-Chung Wang
Chi-Chung Wang
Graduate Institute of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Science,
Fu Jen Catholic University, New Taipei City, Taiwan
Article published in
"Phytomedicine" Volume 49, 1 October 2018, Pages 1-10
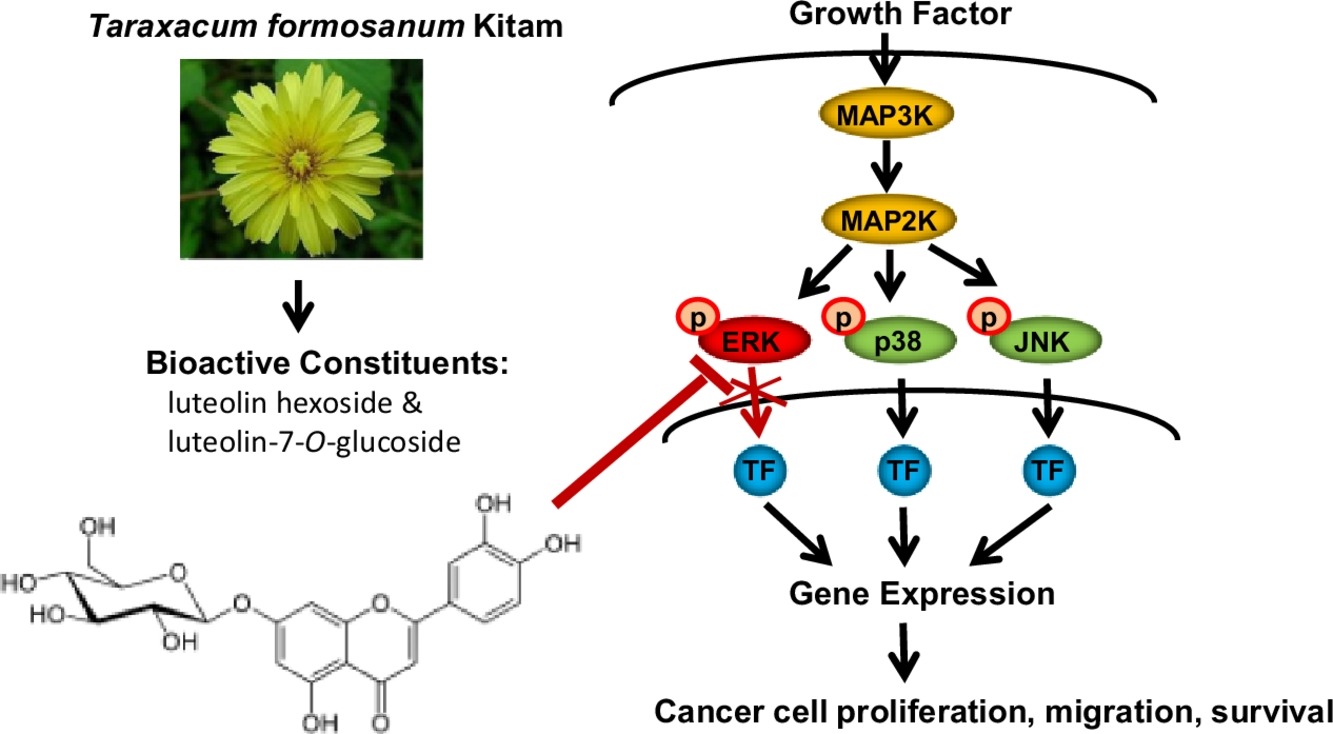
Antioxidant property of Taraxacum formosanum Kitam and its antitumor activity in non-small-cell lung cancer cells
Background
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is known to exhibit resistance to various therapeutic agents and become progressively incurable. Taraxacum formosanum is a medicinal Chinese herb that has been clinically used in Taiwan. However, the investigations of the effects of whole plant on lung cancer are limited.
Purpose
This study evaluated the in vitro antioxidant, antiproliferative, and antimigration effects of the ethanol extract of T. formosanum (ETF). The possible molecular mechanism underlying its antitumor effects on cultured human NSCLC cell lines was also elucidated.
Methods
The antioxidant effects of the ETF were determined using 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) assays, and its antiproliferative and antimigration effects were determined using trypan blue exclusion and wound healing assays, respectively. In addition, changes in the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway were investigated using Western blot analyses. Various inhibitors were used to determine the roles of the MAPK signaling pathway involved in the molecular mechanism of the ETF.
Results
Our results showed that the ETF exhibited strong reducing power, a high Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) value, and potent 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free radical scavenging and Fe+2-chelating abilities. The ETF also exerted antiproliferative and antimigration effects on NSCLC cells in a dose-dependent manner. These effects may be mediated by the inhibitory effects of the ETF on the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase.
Conclusions
This study performed the first pharmacological exploration of T. formosanum. Our results demonstrated the antioxidant and antitumor effects of the ETF on NSCLC cell lines, indicating their potential preventive and therapeutic values for lung cancer.[Full article]